Angular Lazy Loading
Angular Lazy Loading
When you start any angular application. All the NgModules will load whether any module is immediately necessary or not. So by default, loading of NgModule are called eagerly. When you work any large application. you use lot of routes in the application. So it is consider as a lazy loading. To Overcome that problem you can load NgModule as needed. It will help to reduce bundle sizes and decrease load times. In this tutorial, you will see step by step how to impliment lazy loading in application.
Step 1: Craeting an Application
We create creates an application called angularlazyloading and the --routing flag generates a file called app-routing.module.ts. The following CLI command use to create an application and create routing file to define lazy loading lator part of the tutorial.
ng new angularlazyloading --routingNote: --routing option requires Angular version 8.1 or higher version not in lower version.
Step 2: Craeting a module with routing
In this step you need module with a component to route. The following CLI command use to create a module as named Employee with routing.
ng generate module Employee --route Employee
--module app.module The above command create a folder named Employee having the new lazy loadable feature module employee.module.ts. The command automatically declares the EmployeeComponent and imports EmployeeRoutingModule inside the new feature module. --module command option declares by default Employee to route array in app-routing.module.ts.
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { RouterModule, Routes } from '@angular/router';
const routes: Routes = [{ path: 'Employee', loadChildren: () => import('./employee/employee.module').then(m => m.EmployeeModule) }];
@NgModule({
imports: [RouterModule.forRoot(routes)],
exports: [RouterModule]
})
export class AppRoutingModule { }The lazy loading syntax uses loadChildren followed by a function that uses the browser's built-in import(.....)
Step 3: Craeting a new module with routing
Similarly as in step2 you have also created a module named HR.
ng generate module HR --route HR --module app.module
--module command option declares by default Employee to route array in app-routing.module.ts.
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { RouterModule, Routes } from '@angular/router';
const routes: Routes = [{ path: 'Employee', loadChildren: () => import('./employee/employee.module').then(m => m.EmployeeModule) },
{ path: 'HR', loadChildren: () => import('./hr/hr.module').then(m => m.HRModule) }];
@NgModule({
imports: [RouterModule.forRoot(routes)],
exports: [RouterModule]
})
export class AppRoutingModule { }The folder structure of both above CLI command looks like that.

Now add the following code to the app.component.html
<h1>
{{title}}
</h1>
<button type="button" routerLink="/Employee">Employee</button>
<button type="button" routerLink="/HR">HR</button>
<button type="button" routerLink="">Home</button>
<router-outlet></router-outlet>Now Run the application and test it for lazy loading.
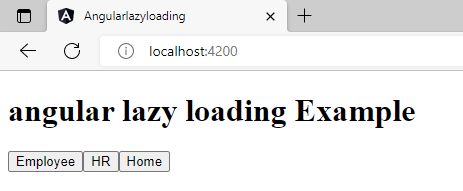
Validating Lazy loading
Now press Ctrl+Shift+j or right click->inspect on a PC and go to the Network Tab.
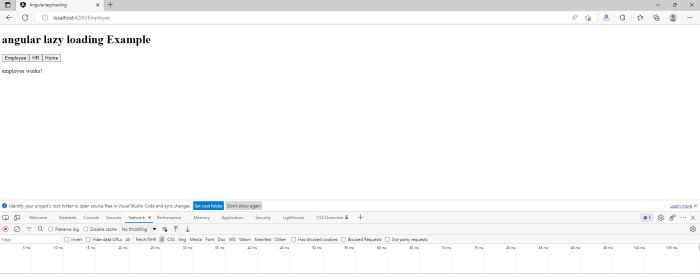
Now click on the emplyee tab it will show only loaded employee module.
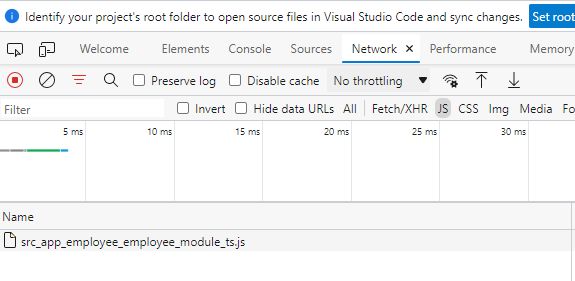
Now click on the delete icon and click on tab HR.
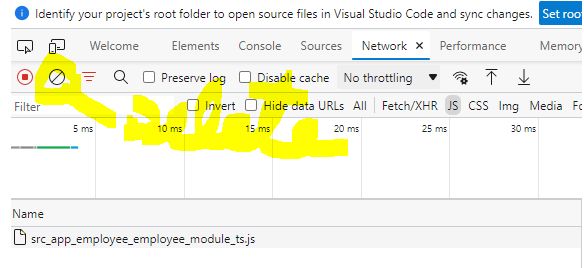
It will load HR module only. So it loaded the module as need.
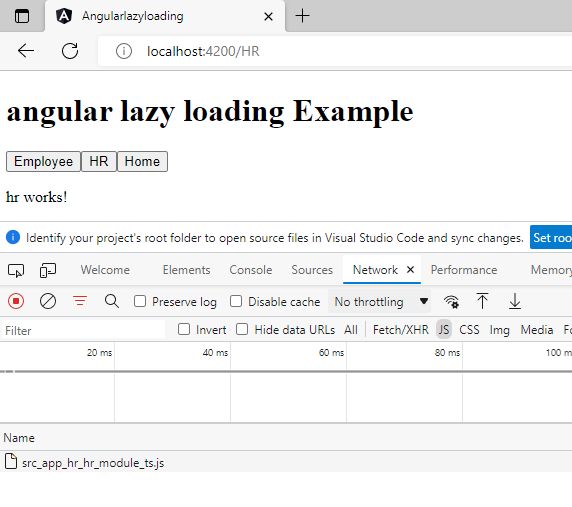
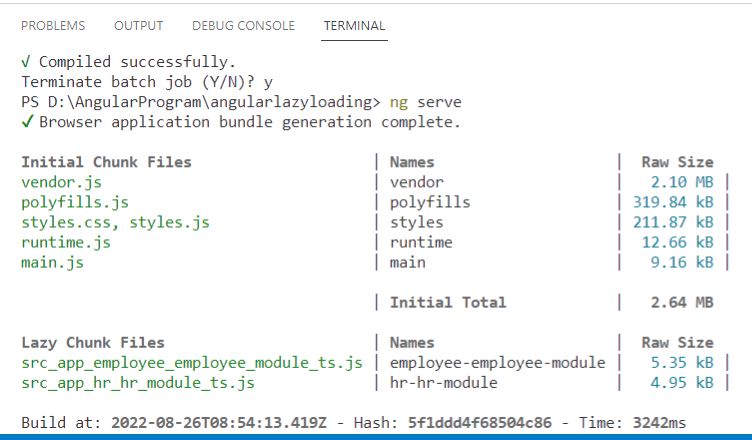
So we can load the module as need in angular using Lazy Loading concept.
Prev Next
