Angular Dependency Injection
In this tutorial we'll see how depandency take place in our code and how remove it through dependency injection.
Angular Dependency Injection
Dependency Injection is used to make a class independent of its dependencies. Dependency Injection (DI) is a technique in which a class receives its dependencies from outside sources of a class rather than creating them inside class.
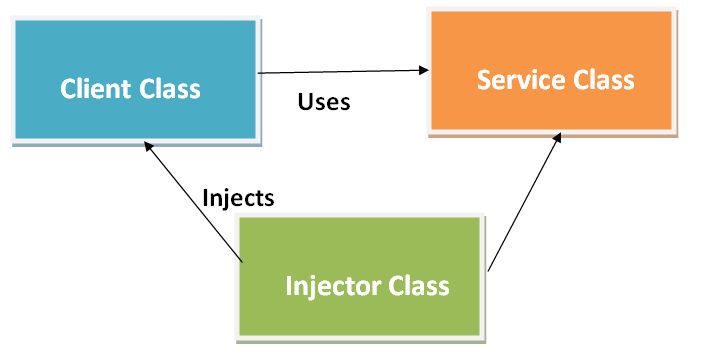
The above image show the following three things:
- Client Class - This is the dependent class which depends on the service class.
- Service Class - This Class is used to provide the service to the client class.
- Injector Class - This class is used to inject the service class object into the client class.
Dependency injection has the following benefits as below.
- Reduced Dependencies.
- It Enables clean code
- It Enables unit testing
- It Encourages decoupling
- More Reusable Code
Angular Dependency Injection Types
There are three types of Angular Dependency Injections as shown in below image.
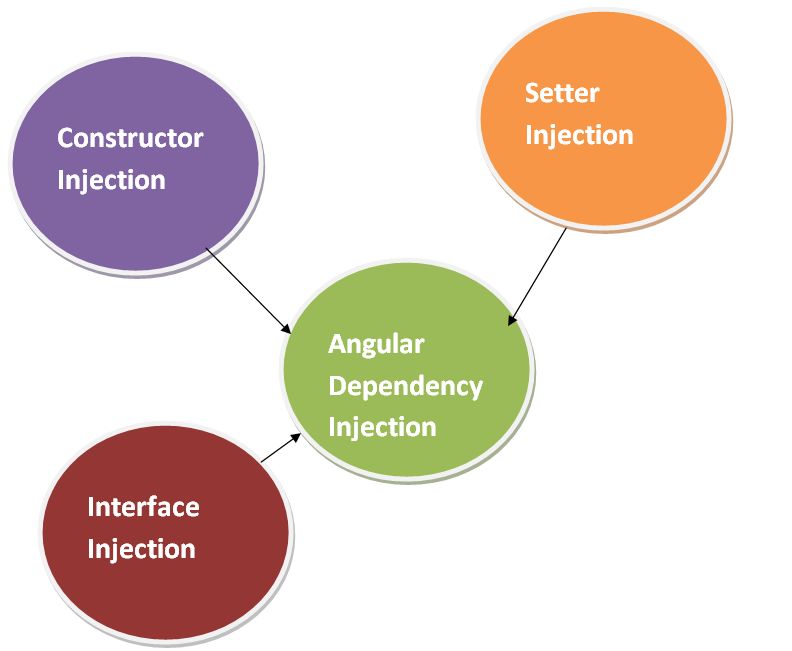
- Constructor injection- It is used to provide the dependencies through a class constructor.
- Setter injection - The client class uses a setter method into which the injector injects the dependency.
- Interface injection - The clients will be implement an interface that exposes a setter method that accepts the dependency.
Now firstly we 'll understand how dependency take place inside our angular class and also see how we can remove dependeny through Constructor Injection.
Angular Service
When you develop a project many times developers use the same code again and
again. In angular also repetitive code in multiple components becomes difficult
to manage the code. It will increase the size of the angular project or
application. So you need to write such a code which will reusable. To handle
that type of situation in angular you can create Services class. In an
angular application, the service is responsible for providing the data to the
component or specific component task.
Read More.....
Why need Angular Dependency Injection
Create an application
The following command uses the Angular CLI to create a Angular application. The application name in the following example is angularDependencyInjection.
ng new angularDependencyInjectionCreating an Service
The following command uses the Angular CLI to create service. The service name Employee in the following example:
ng g service EmployeeNow open the service file employee.service.ts looks like that:
import{ Injectable } from @angular/core';
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root'
})
export class EmployeeService {
constructor() { }
}Add the following code with employee service
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root'
})
export class EmployeeService {
getAllemployee() {
return [
{
ID: '1', Name: 'Rohatash', Gender: 'Male'
},
{
ID: '2', Name: 'Rajesh', Gender: 'Male'
},
{
ID: '3', Name: 'Rahul', Gender: 'Male'
},
{
ID: '4', Name: 'Ritesh', Gender: 'Male'
},
{
ID: '5', Name: 'Ravindar', Gender: 'Male'
},
{
ID: '6', Name: 'Deepak', Gender: 'Male'
},
{
ID: '7', Name: 'Manoj', Gender: 'Male'
},
{
ID: '8', Name: 'Deepali', Gender: 'Female'
}
]}
}
The @Injectable decorator accepts a metadata object for the service. @Injectable() Decorator that marks a class as available to be provided and injected as a dependency.
Now we create a object of EmployeeService class in app.component.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { EmployeeService } from './employee.service';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})
export class AppComponent {
employee:any = [];
EmployeeService;
constructor(){
this.EmployeeService = new EmployeeService(); // Creating Object of EmployeeService class
}
getEmployeelist() {
this.employee= this.EmployeeService.getAllemployee(); // Calling Method of service class
}
}In the above code The AppComponent is now tightly coupled to the EmployeeService, This create lot of Issues as explained below.
- The EmployeeService is used as hardcode in our AppComponent. What if we want to use ListEmployeeService. We need to change wherever the EmployeeService is used and rename it to ListEmployeeService.
- Suppose EmployeeService depends on another Service. And then we decide to change the service to some other service. So need to update code manually.
- In the above code we'll see Component Class has tied one particular implementation of EmployeeService . It will make it difficult to reuse our components.
To solve all these above problems.
Remove Dependency Injection through Constructor
Add the following service reference in app.module.ts inside provider.
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { AppRoutingModule } from './app-routing.module';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import { EmployeeService } from './employee.service';
@NgModule({
declarations: [
AppComponent
],
imports: [
BrowserModule,
AppRoutingModule
],
providers: [EmployeeService],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
export class AppModule { }
we'll create EmployeeService to the constructor the AppComponent class as shown below.
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { EmployeeService } from './employee.service';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})
export class AppComponent {
employee:any = [];
constructor(private _EmployeeService: EmployeeService) { } // Created constructor for service
getEmployeelist() {
this.employee= this._EmployeeService.getAllemployee(); // Call the service
}
}
Now need to add the service in app.component.html
<h2>Example of dependency Injection</h2>
<div><button type="button" (click)="getEmployeelist()" style="background-color:chartreuse">Get Employeee List</button></div>
<br><br>
<table border="1" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0">
<thead>
<tr style="background-color:blue; color:white">
<th>Employee ID</th>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Gender</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr *ngFor='let empobj of employee'>
<td>{{empobj.ID }}</td>
<td>{{empobj.Name }}</td>
<td>{{empobj.Gender }}</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>Now run the application.
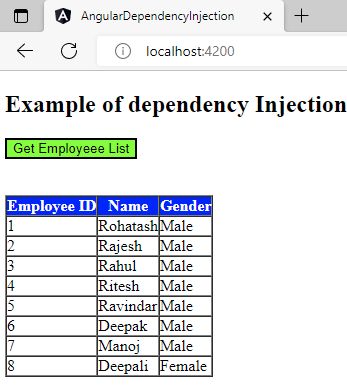
Now click on the button. It will show all the employee list.
Prev Next
