`
OOPs - Introduction
In this article we are going to discuss what is the OOPs(Object-Oriented Programming). There are many blogs, articles are available on the internet regarding OOPs but in this particular article I will try to explain to you with as much as simplest and realistic examples so you can get a clear idea of the OOPs concepts.
OOPs(Object-Oriented Programming) Introduction
- OOP stands for Object-Oriented Programming, which means it is a way to create software around objects.
- OOPs refers to languages that use objects in programming.
- OOPs provide a clear structure for the software's and web applications.
- OOP languages enable programmers to create modules that can be reused in different parts of an application or in future applications.
- The main aim of OOP is to bind together the data and the functions that operate on them so that no other part of the code can access this data except that function.
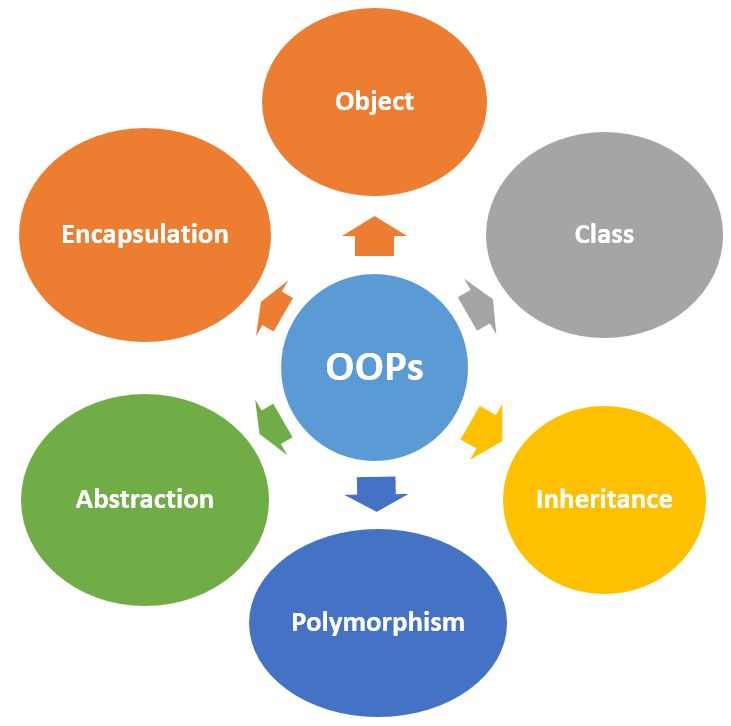
OOPs Concepts
The following are the main concept or pillar of OOPs. In Later Articles we will discuss these points one by one.
Advantages of OOPs
The following are the advantages of OOPs.
- Easier troubleshooting throuth Modularity - Objects are
self-contained, and each piece of functionality is defined in a single
object. This makes the code more modular and easier to understand,
which in turn makes it easier to maintain and debug. - Reuse of code through inheritance - Inheritance allows new objects to take on properties of existing objects. This feature helps in reducing redundancy in code, which can make a system easier to modify and maintain.
- Objects and classes can be reused in different programs - TO save development time and reducing errors. This means that once an object is created, it can be reused across multiple projects. The more reusable the code is, the less code developers have to write from scratch.
- Flexibility of code using polymorphism - Polymorphism allows the same function or method to work in different ways for different objects. This means that a single interface can cater to different data inputs, reducing the need for coding all possible scenarios.
- Easily scalable - Object-oriented systems can be easily upgraded from small to large systems.
- Better Data Security - With encapsulation, OOP ensures that data is not accessible to the outside world and only those functions which are wrapped in the class can access it. This helps in protecting the data from unintended modifications.
- Save Development Time - With features like code reusability and modularity, developers can save time during the development process.
Disadvantage or limitations of OOPS
The following are the disadvantages of OOPs.
- Complex to Understand - OOP can be more complex to understand compared to procedural programming. The concepts of inheritance, polymorphism, and encapsulation, while powerful, can be abstract and difficult for newcomers.
- Slower execution of the Code - The length of the programmes developed using OOP language is much larger than the procedural approach. Since the programme becomes larger in size, it requires more time to be executed thatleads to slower execution of the programme
- Memory Usage - Object-oriented programs often require more memory than procedural equivalents. This is because of the additional information (like method tables) that needs to be stored alongside objects.
- Complexity in Design - Poorly designed object-oriented systems can become overly complex, with too many classes, interrelationships, leading to code that is hard to understand, maintain, and modify.
- Understand Object - Everything is treated as object in OOP so before applying it we need to have excellent thinking in terms of objects.
- It is not suitable for small applications.
Next
