JavaScript Interview Question
1. What is JavaScript?
JavaScript was invented by Brendan Eich in 1995, and became an ECMA standard in 1997. JavaScript is a lightweight client-side scripting language that is open-source and allows cross-platform. It doesn’t require compilation and is interpreted with object-oriented capabilities. Also, it works with various other programming languages. And this is the reason for its vast use all around the world. Many popular websites and web applications like Google, Amazon, PayPal, etc use this language. The file extension of a JavaScript file is .js. It is supported by virtually all web browsers available today, such as Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Apple Safari, etc.
2. What is the difference between null and undefined in JavaScript?
In JavaScript, Null is used to define absence of a value or it is an empty value.Variable declared and is an empty value. It accepts only one value which is null. The variable to represent no value it is an object. Undefined is used to define missing of a value or it is an empty value. Variable has been given a space in memory, but no value is assigned to it. This type we can not used as assign value.
3. What is a closure in JavaScript?
A closure is an inner function that has access to the variables and parameters of its outer function, even after the outer function has returned.
4. What is the difference between let and var in JavaScript?
The main difference between let and var in JavaScript is that let has block scope, while var has function scope.
| SNo. | Var Keyword | Let Keyword |
| 1 | The Var keyword introduce in JavaScript before the advent of ES6. | The Let keyword introduce in JavaScript in the advent of ES6 |
| 2 | Var declarations can be globally or function scoped. | The Let keyword scope is limited to block scope |
| 3 | Var can be Redeclared | The Let can not Redeclared |
| 4 | Var can be updated | The Let can be updated |
| 5 | Hosting of Var means declarations of variales and function should be before execution of code. It is initialized as undefined | Hosting of Var means declarations of variales and function should be before execution of code. It is left as uninitialized |
5. What is the difference between == and === operators in JavaScript?
The == operator compares the values of two variables, while the === operator compares both the values and the types of the variables.
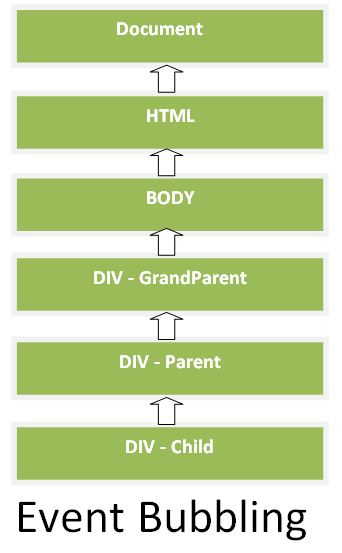
6. What is event bubbling in JavaScript?
In bubbling, the event starts at the target element and then "bubbles" up to all of its ancestor elements. While developing a webpage or a website via JavaScript, the concept of event bubbling is used where the event handlers are invoked when one element is nested on to the other element and are part of the same event. This technique or method is known as Event Bubbling.
We can also understand the flow of Bubbling event with the help of the below flow chart.
7. What is the difference between synchronous and asynchronous programming in JavaScript?
Synchronous programming is when each task is executed in order, one after the other, while asynchronous programming allows multiple tasks to be executed simultaneously.
8. What are callbacks in JavaScript?
JavaScript statements are executed line by line. However, with effects, the next line of code can be run even though the effect is not finished. This can create errors. To prevent this, you can create a callback function. A callback function is executed after the current effect is finished.
9. What is hoisting in JavaScript?
JavaScript hoisting is a behavior in which variable and function declarations are moved to the top of their respective scopes during the compilation phase, before the code is executed. This means that variables and functions can be used before they are actually declared in the code.
For example, consider the following code:
console.log(x); // undefined
var x = 5;
In this code, the console.log statement will output undefined because the variable x is declared with the var keyword, which is hoisted to the top of the scope. However, the assignment x = 5 is not hoisted, so the value of x is undefined until it is assigned later in the code.
10. What is the use of the "this" keyword in JavaScript?
The "this" keyword in JavaScript refers to the object that is currently executing the function and is used to access and manipulate properties and methods of that object.
11. What is the difference between let and const in JavaScript?
The main difference between let and const in JavaScript is that let variables can be reassigned, while const variables cannot be reassigned.
12. What is the difference between a let and a var variable?
The main difference between a let and a var variable is that let has block scope, while var has function scope.
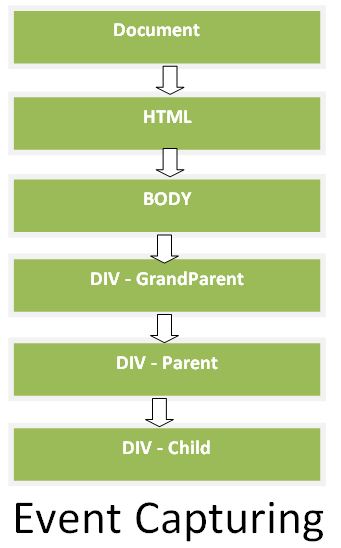
13. What is event capturing in JavaScript?
Event Capturing is also known as Event Trickling. Event Capturing is opposite to event bubbling, where in event capturing, an event moves from the outermost element to the target. In capturing, the event starts at the document object and then "captures" its way down to the target element.
We can also understand the flow of Capturing event with the help of the below flow chart.
14. What are arrow functions in JavaScript?
Arrow functions are a shorthand notation for creating anonymous functions in JavaScript.
15. What are template literals in JavaScript?
Template literals are a way to embed expressions inside a template string in JavaScript.
16. What is the difference between call and apply in JavaScript?
The call() method and the apply() method in JavaScript are used to set the value of "this" inside a function and to pass arguments to that function.
17. What is the difference between a function declaration and a function expression in JavaScript?
A function declaration is a named function that is defined using the "function" keyword, while a function expression is an unnamed function that is defined using a variable assignment.
18. What is the difference between let and var in terms of hoisting?
Both let and var are hoisted in JavaScript, but var is initialized to "undefined" while let is not initialized.
19. What are the advantage of JavaScript?
Let’s start off with the benefits of JavaScript that make it superior to other programming languages.
- Speed - It is a client-side script that shortens the time required to establish a server connection, which speeds up program execution.
- Reduces load on the server - The language runs on the client side rather than the server. Thus, the server doesn’t have to deal with the stress of executing JavaScript
- Ease of use - JavaScript is one of the simplest languages to learn, particularly for web programming. Since difficult languages have fewer engineers and demand a higher budget, this helps web companies save a lot of money on development.
- Rich Interface - JavaScript offers developers a variety of interfaces to build engaging websites like drag-and-drop elements or sliders. This increases user interaction with the website.
- Interoperability - JavaScript seamlessly integrates with other programming languages, so many developers favour using it to create various apps.
- Popularity - JavaScript is one of the most popular languages for web development. It is used almost for every working website.
- Platform independence - Most browsers support JavaScript, making it simple for any browser to comprehend and recognise JavaScript code. Updates - 13 editions of features have been released since 1997.
20. What is the purpose of the "use strict" directive in JavaScript?
It was introduced in ECMAScript 5 to address to make it easier to write secure code. The JavaScript provides "use strict"; expression to enable the strict mode. If there is any silent error or mistake in the code, it throws an error.
21. What is an IIFE in JavaScript?
An IIFE (Immediately Invoked Function Expression) is a function that is executed immediately after it is defined.
22. What is the difference between "var" and "let" in JavaScript?
The main difference between "var" and "let" in JavaScript is that "var" has function scope, while "let" has block scope.
23. What is a promise in JavaScript?
A promise in JavaScript is an object that represents the eventual completion or failure of an asynchronous operation and its resulting value.
24. What is the difference between "undefined" and "null" in JavaScript?
"undefined" means that a variable has been declared but has not been assigned a value, while "null" is an explicit assignment of a non-value.
25. What is the difference between "const" and "let" in JavaScript?
The main difference between "const" and "let" in JavaScript is that "const" variables cannot be reassigned, while "let" variables can be reassigned.
26. What is the purpose of the "async" keyword in JavaScript?
The "async" keyword in JavaScript is used to define an asynchronous function that returns a Promise.
27. What is the purpose of the "await" keyword in JavaScript?
The "await" keyword in JavaScript is used to wait for a Promise to resolve before continuing with the execution of the code.
28. What is the difference between "var" and "let" in terms of hoisting?
Both "var" and "let" are hoisted in JavaScript, but "var" is initialized to "undefined" while "let" is not initialized.
29. What is the difference between "var" and "const" in JavaScript?
The main difference between "var" and "const" in JavaScript is that "const" variables cannot be reassigned, while "var" variables can be reassigned.
30. What is the difference between a shallow copy and a deep copy in JavaScript?
A shallow copy in JavaScript creates a new object with the same properties as the original object, while a deep copy creates a new object with new copies of all the properties and values of the original object.
31. What is the difference between "null" and "undefined"?
"null" is an explicit assignment of a non-value, while "undefined" means that a variable has been declared but has not been assigned a value.
32. What is the difference between "let" and "const" in terms of scope?
Both "let" and "const" have block scope in JavaScript.
33. What is a generator function in JavaScript?
A generator function is a special function in JavaScript that can be paused and resumed, allowing for iterative operations.
34. What is the difference between "continue" and "break" in JavaScript?
"continue" is used to skip a single iteration of a loop, while "break" is used to exit a loop entirely.
35. What is a higher-order function in JavaScript?
A higher-order function is a function that takes other functions as arguments or returns functions as its result.
36. What is the difference between "var" and "let" in terms of redeclaration?
"var" can be redeclared in the same scope, while "let" cannot be redeclared in the same scope.
37. What is the difference between a constructor function and a class in JavaScript?
A constructor function is a function used to create objects, while a class is a template for creating objects.
38. What is the difference between a prototype and a constructor in JavaScript?
A prototype is a property of a function that allows for the creation of new objects with the same properties and methods as the original object, while a constructor is a function used to create objects.
39. What is the difference between "var" and "let" in terms of global scope?
Both "var" and "let" can be declared in global scope in JavaScript.
40. What is a callback function in JavaScript?
A callback function is a function that is passed as an argument to another function and is executed after an asynchronous operation has completed.
41. What is a pure function in JavaScript?
A pure function is a function that always returns the same output for the same input and has no side effects.
42. What is a prototype in JavaScript?
A prototype is a property of a function that allows for the creation of new objects with the same properties and methods as the original object.
43. What is a getter and a setter in JavaScript?
JavaScript provides several methods for adding, removing or changing an HTML element's attribute. You can get and set the attributes of HTML elements using the DOM (Document Object Model).
Here, are some common methods for getting and setting attributes.
- Get an attribute
- Set an attribute
- Remove an attribute
- Get or set the content of an element
Prev Next
