JavaScript Introduction
JavaScript was invented by Brendan Eich in 1995, and became an ECMA standard in 1997. JavaScript is a lightweight client-side scripting language that is open-source and allows cross-platform. It doesn’t require compilation and is interpreted with object-oriented capabilities. Also, it works with various other programming languages. And this is the reason for its vast use all around the world. Many popular websites and web applications like Google, Amazon, PayPal, etc use this language. The file extension of a JavaScript file is .js. It is supported by virtually all web browsers available today, such as Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Apple Safari, etc.
JavaScript provides client-side form validation and works instantly to validate the contents of a web form rather than making a round-trip to the server.
Why is it called JavaScript?
When JavaScript was created, it initially had another name - LiveScript. But Java was very popular at that time, so it was decided that positioning a new language as a younger brother of Java would help. But as it evolved, JavaScript became a fully independent language with its own specification called ECMAScript, and now it has no relation to Java at all.
Why do we need JavaScript?
Most applications work due to an interaction between a client (user's device) and a remote server. The client requests data from the server. The server receives the request, processes it and then responds accordingly. The response sent back is in a user-readable format and is thus acceptable by the client. But this process takes time as well as resources. Although we usually need this connection, in some projects, JavaScript often helps to avoid it.
JavaScript allows the validation of forms without the input of the server, reducing traffic. It provides wonderful tools for a more interactive and user-friendly website. Some of the basic functions of JavaScript are:
- Autocomplete: The search box gives suggestions, based on what the user has already typed.
- Form validation: If the users make a mistake while filling a form, JavaScript immediately informs them of the error, avoiding to fill it all again.
- Fixes layout issues to avoid the overlapping of elements on the page.
- Adds animation to the page to make it more attractive.
What makes JavaScript unique?
There are at least three great things about JavaScript:
Full integration with HTML/CSS. Simple things are done simply. Supported by all major browsers and enabled by default.
JavaScript is the only browser technology that combines these three things.
Advantages of JavaScript
Let’s start off with the benefits of JavaScript that make it superior to other programming languages.
- Speed - It is a client-side script that shortens the time required to establish a server connection, which speeds up program execution.
- Reduces load on the server - The language runs on the client side rather than the server. Thus, the server doesn’t have to deal with the stress of executing JavaScript
- Ease of use - JavaScript is one of the simplest languages to learn, particularly for web programming. Since difficult languages have fewer engineers and demand a higher budget, this helps web companies save a lot of money on development.
- Rich Interface - JavaScript offers developers a variety of interfaces to build engaging websites like drag-and-drop elements or sliders. This increases user interaction with the website.
- Interoperability - JavaScript seamlessly integrates with other programming languages, so many developers favour using it to create various apps.
- Popularity - JavaScript is one of the most popular languages for web development. It is used almost for every working website.
- Platform independence - Most browsers support JavaScript, making it simple for any browser to comprehend and recognise JavaScript code. Updates - 13 editions of features have been released since 1997.
Disadvantages of JavaScript
It’s not always the best practice to use JavaScript when developing online applications. In many circumstances, JavaScript might not function as well as some of the other languages. The issues with JavaScript have been briefly discussed in this section.
Here are some potential disadvantages of using JavaScript:
- Browser Compatibility - JavaScript code can behave differently across different web browsers. This can make it difficult to ensure that your code works consistently across different platforms.
- Security - JavaScript is executed on the client-side, which means that it's possible for malicious users to modify the code and potentially compromise the security of your application.
- Performance - JavaScript is an interpreted language and can be slower than compiled languages like C or Java. However, modern JavaScript engines have made significant improvements in performance.
- Lack of Type Safety - JavaScript is a dynamically typed language, which means that it's possible to assign a value of one type to a variable of another type. This can lead to unexpected behavior and errors.
- Debugging - Debugging JavaScript code can be challenging, especially in complex applications. There are tools available to help with this, but it still requires a significant amount of effort to locate and fix bugs.
Applications of JavaScript
The following are the applications of JavaScript.
- Web Development
- Web Applications
- Presentations
- Server Applications
- Web Servers
- Games
- Art
- Smartwatch Applications
- Mobile Applications
- Compiler
- Embedded Systems
- Operating Systems
- Data Science
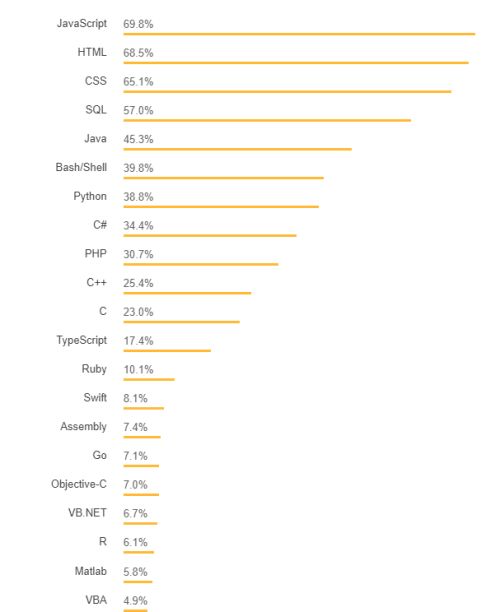
JavaScript Popularty Graph
According to the Stack Overflow survey, 69% of respondents said they had used JavaScript in their projects. JavaScript is the most commonly used programming language.
Next
