Generics Introduction
In this article we are going to discuss how to implement Generics in class and method level with examples in C#.
Generic Introduction
Generics in C# are a powerful feature that allows you to define classes, interfaces, and methods with a placeholder for the type of data they store and manipulate. This placeholder can then be replaced with any data type you specify when you create an instance of the generic type or call a generic method. Generics provide type safety without the need to know the actual data type at compile time.

Here, we will see.
- Generic Class in C#
- Generic Mehod in C#
- Constraints on Generics in C#
- Generic Class with Constraints
- Generic Method with Constraints
1. Generic Class in C#
To define a generic class, you use angle brackets (< >) to
specify a placeholder (or placeholders) for the type(s) the class will operate
on. The placeholder is typically a single letter like T, but you
can use any identifier.
Here's an example of using a generic class in C#. In this example we create a generic class and defind placeholder(T) and create a constructor of class.
using System;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
public class GenericClass<T>
{
private T _value;
public GenericClass(T value)
{
_value = value;
}
public T GetMethod()
{
return _value;
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
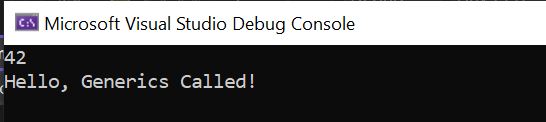
GenericClass<int> intInstance = new GenericClass<int>(42);
Console.WriteLine(intInstance.GetMethod()); // Outputs: 42
GenericClass<string> stringInstance = new GenericClass<string>("Hello, Generics Called!");
Console.WriteLine(stringInstance.GetMethod()); // Outputs: Hello, Generics Called!
}
} Output
2. Generic Mehod in C#
Generic methods allow you to define methods with type parameters, enabling them to operate on different data types. Here's an example of using a generic method that add two numbers in C#.
using System;
public class Utilities
{
public T Add<T>(T first, T second)
{
dynamic a = first;
dynamic b = second;
return a + b;
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Utilities obj1=new Utilities();
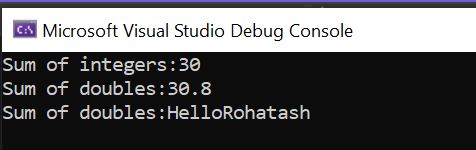
Console.WriteLine($"Sum of integers:" + obj1.Add(10, 20));
Console.WriteLine($"Sum of doubles:" + obj1.Add(10.5, 20.3));
Console.WriteLine($"Sum of doubles:" + obj1.Add("Hello", "Rohatash"));
}
} Output
3. Constraints on Generics in C#
Sometimes, you may want to restrict the types that can be used with your generic class or method. You can use constraints to specify these restrictions.
- Generics can be applied to both value types and reference types.
- Use
structconstraint for value types andclassconstraint for reference types. - Constraints help to enforce specific requirements on the types used with generics.
Generic Class with Constraints - Where T : struct
To specify that a type parameter must be a value type, use the struct constraint.
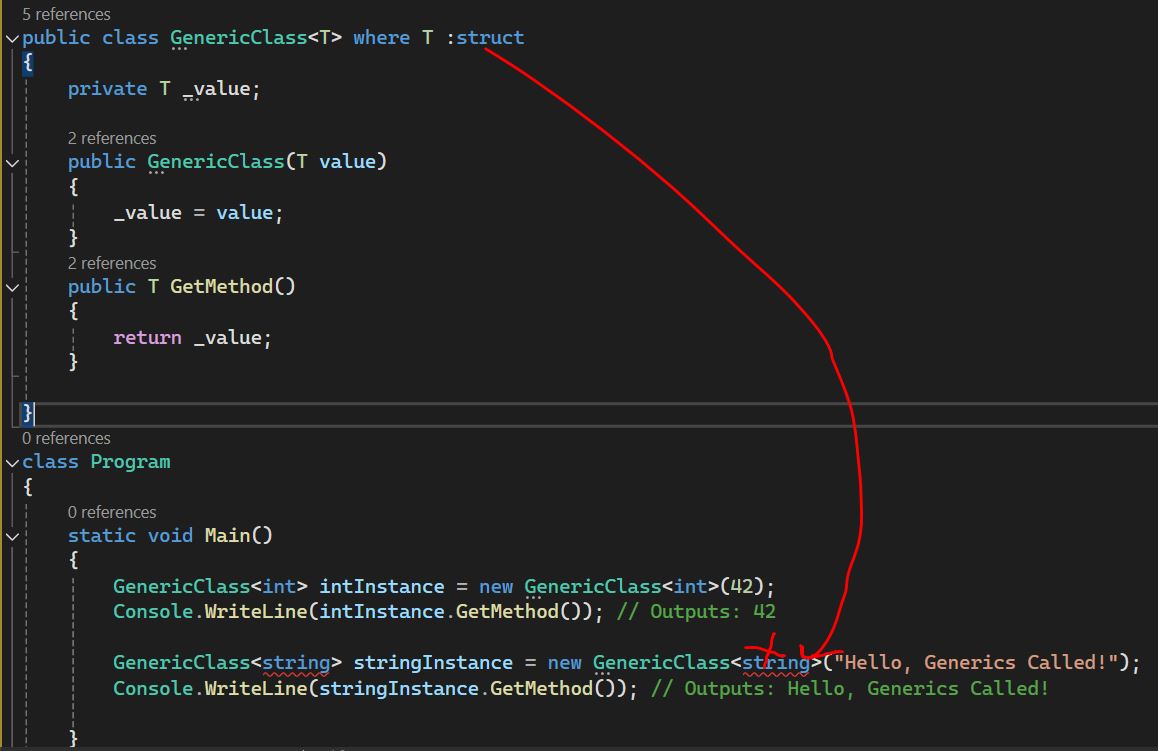
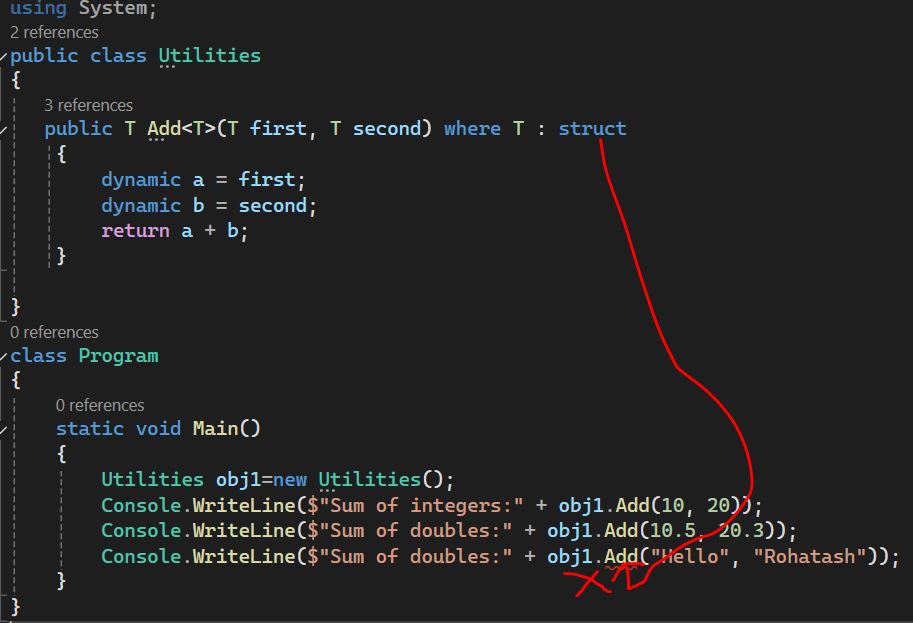
This will cause a compile-time error because string is a reference type and we have used struct which is value type. So for int it will work but not for string type.
Generic Class with Constraints - Where T : class
To specify that a type parameter must be a reference type, use the class constraint.
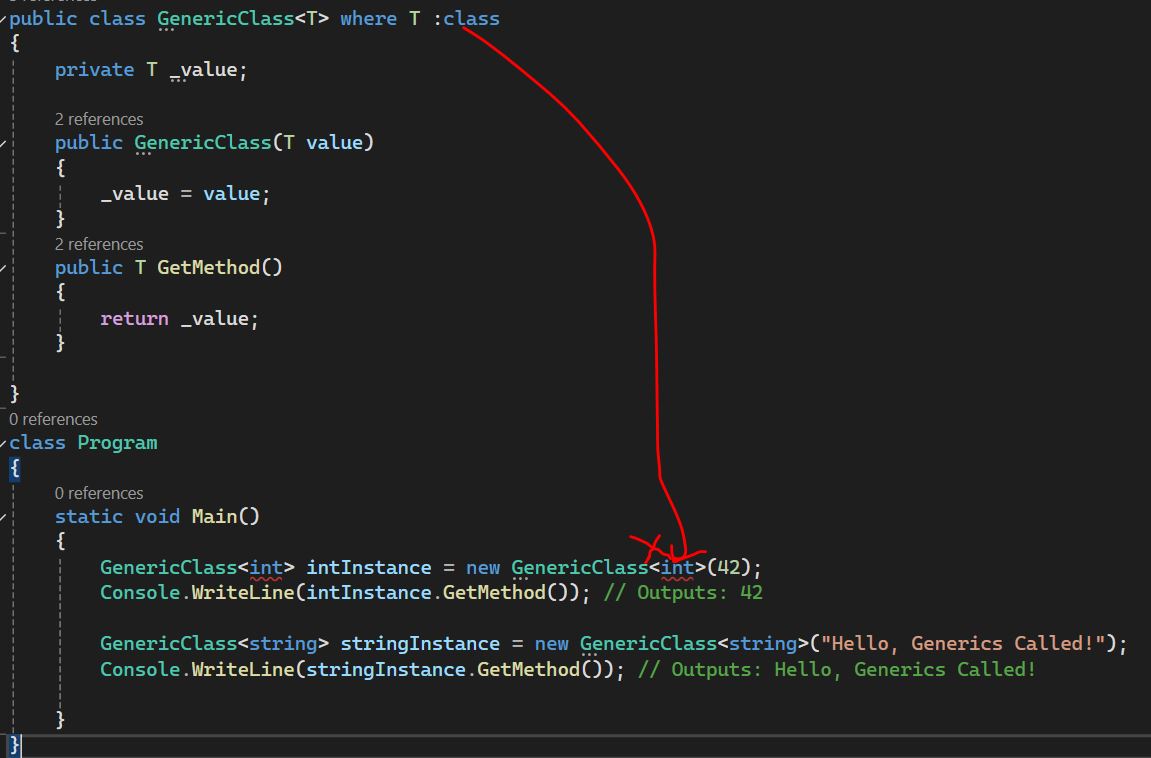
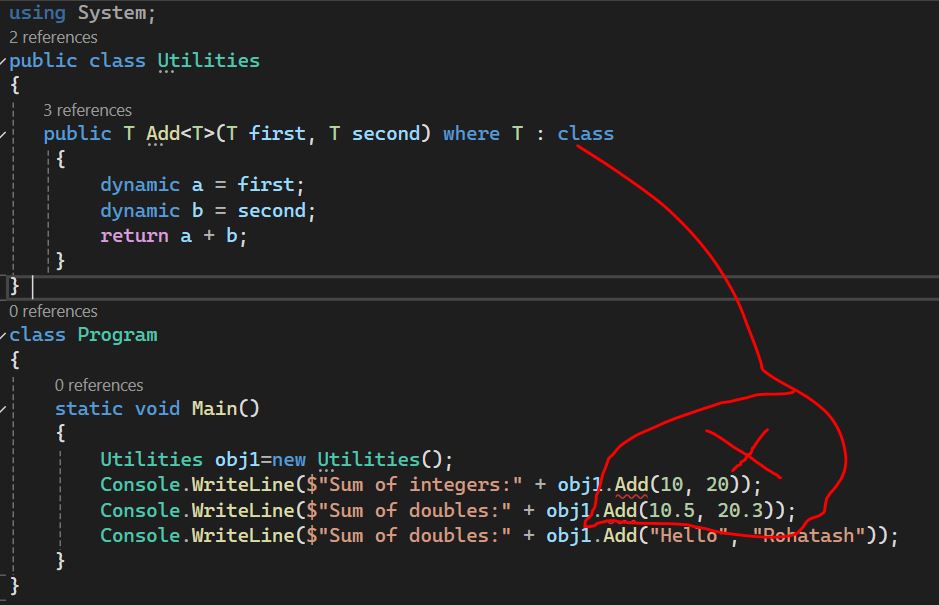
This will cause a compile-time error because int is a value type and we have used class which is reference type. So for string it will work but not for int type.
Generic Method with Constraints
You can also apply constraints to type parameters in generic methods to specify requirements for the types that can be used. you might want to restrict a type parameter to reference types or types that implement a specific interface.
Generic Method with Struct Constraint
Here is an example of a generic method that requires the type parameter to be a value type - struct.
Generic Method with Class Constraint
Here is an example of a generic method that requires the type parameter to be a reference type - class.
Advantage of Generics
- Type Safety - Generics ensure that you can only use the type specified when creating the instance, which reduces runtime errors.
- Performance - Generics eliminate the need for boxing and unboxing when working with value types, as well as the need for type casting.
- Code Reusability - Generics allow you to write more flexible and reusable code. You can define a single class or method that works with any data type.
- Maintainability - Generics can help reduce code duplication, making your code easier to maintain.
Where need to Use Generics?
- Classes and Interfaces - You can create classes and interfaces that operate on any data type, such as a Repository<T> for data access or a Comparer<T> for custom comparison logic.
- Methods - Generic methods enable you to create a method that can operate on different types, such as sorting, searching, or swapping elements in an array.
- Collections - The most common use of generics in C# is with collections, such as List<T>, Dictionary<TKey, TValue>, and Queue<T>. These classes allow you to create collections of any type.
Prev Next
