Inheritance
In this article we are going to discuss the Inheritance in C#. There are many blogs, articles are available on the internet regarding Inheritance but in this particular article I will try to explain to you with as much as simplest and realistic examples so you can get a clear idea of the Inheritance in C#.
Inheritance Introduction
It is a parent-child relationship. In C#, it is possible to inherit fields and methods from one class to another. We group the inheritance concept into two categories.
- Base Class (parent) - The class whose features are inherited is known as super class(or a base class or a parent class).
- Derived Class (child) - The class that inherits the other class is known as subclass(or a derived class, extended class, or child class). The subclass can add its own fields and methods in addition to the superclass fields and methods.
The following figure shows the hierarchy of Parent and child class in C#.
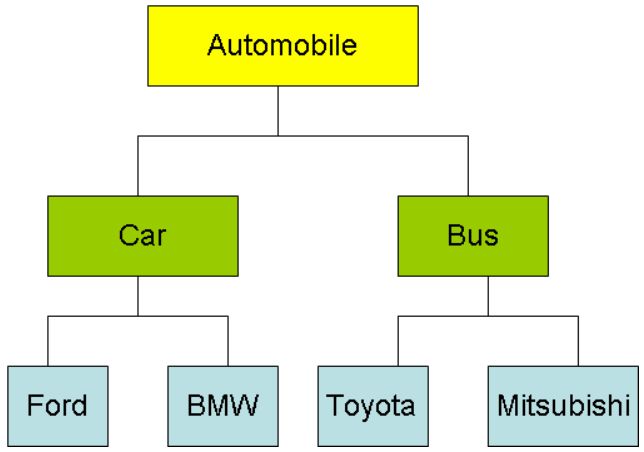
In the above example, the Car and Bus classes inherit the characteristics of the Automobile class. The Automobile class is the superclass of the Car and Bus classes as its subclass.
To inherit from a class, use the :symbol.
Some important key point related to Inheritance
- The new class inherits the properties and methods of the existing class and can also add new properties and methods of its own. Inheritance promotes code reuse, simplifies code maintenance, and improves code organization.
- In Inheritance, the child class can consume members of its parent class if it is the Owner of those members.
- In the Inheritance child class can not consume private members of its parent class.
- Parent classes constructor must be accessible to the child class. Otherwise, Inheritance is not possible.
- In Inheritance, the child class can access parent class members, but parent classes can never access any child class members.
- In C#, we don't support multiple Inheritance through classes. But we can achieve this using Interface.
- Inheritance mainly used for code reuse, simplifies code maintenance, and improves code organization.
Inheritance Example
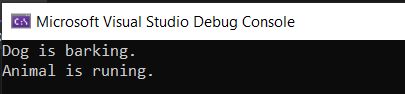
In the example below, the Dog class (child) inherits the fields and methods from the Animal class (parent):
class Animal //base class (parent)
{
public void Run() //Animal method
{
Console.WriteLine("Animal is runing.");
}
}
class Dog : Animal //derived class (child)
{
public void Bark() //Dog method
{
Console.WriteLine("Dog is barking.");
}
}
// Example usage
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create an instance of the Dog class
Dog myDog = new Dog();
// Call methods from the Dog class
myDog.Bark();
// Call inherited method from the Animal class
myDog.Run();
}
}Output
Sealed Keyword in C#
If you don't want other classes to inherit from a class, use the sealed keyword. If you try to access a sealed class, C# will generate an error.
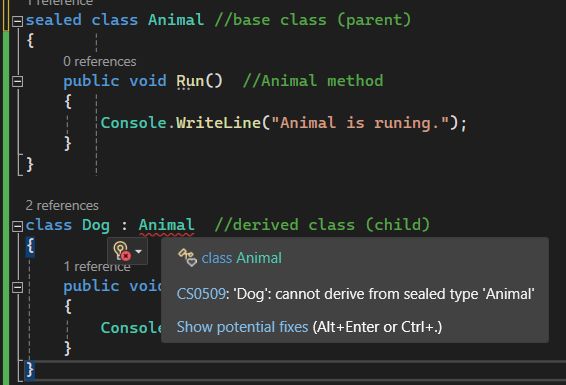
The error message will be something like this.
Static Keyword in C#
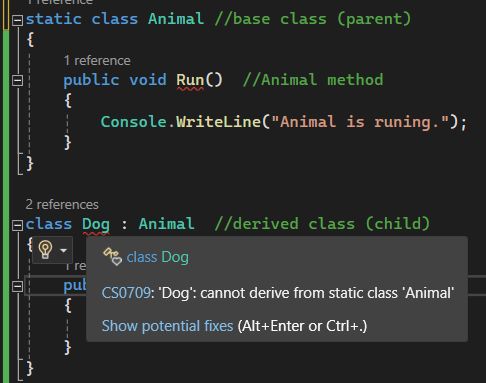
If you don't want other classes to inherit from a class, use the Static keyword. If you try to access a Static class, C# will generate an error.
Why do We Use Inheritance?
The answer is reusability. One of the key features of a modern programming language is code reusability. Multiple applications and programs can use a piece of code written by one developer if it provides the same functionality. It not only saves time but also reduces the size of the code. That helps program maintainability and improves reusability.
Example
When you created a Calculator class that has the functionality of adding, subtracting, dividing, and multiplying. Now, other programs implement an advanced calculator with conversion functionality and advanced calculations with basic functionality. They can derive their classes from the Calculator class.
Advantages of Inheritance
- Code Reusability - Inheritance allows us to reuse existing code by inheriting properties and methods from an existing class.
- Code Maintenance - Inheritance makes code maintenance easier by allowing us to modify the base class and have the changes automatically reflected in the derived classes.
- Code Organization - Inheritance improves code organization by grouping related classes together in a hierarchical structure.
Disadvantages of Inheritance
- Tight Coupling - Inheritance creates a tight coupling between the base class and the derived class, which can make the code more difficult to maintain.
- Complexity - Inheritance can increase the complexity of the code by introducing additional levels of abstraction.
- Fragility - Inheritance can make the code more fragile by creating dependencies between the base class and the derived class.
Next
