C# Loops
In programming, loops are control structures that allow a set of instructions to be repeated multiple times. Loops are used to iterate over a collection of data, perform a set of operations a certain number of times, or until a specific condition is satisfied.
Real World Examples of Loops
Suppose you run a website that sells products, and you want to display the names and prices of all the products in your catalog on a webpage. You have an array of objects called products that contains the name and price of each product. You can use a for loop in C# to iterate through the array and display the name and price of each product.
Here's an example of what the loop might look like:
public class Product
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public double Price { get; set; }
public Product(string name, double price)
{
Name = name;
Price = price;
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
List products = new List
{
new Product("Product A", 15),
new Product("Product B", 25.99),
new Product("Product C", 20.99),
new Product("Product D", 25.99)
};
for (int i = 0; i < products.Count; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{products[i].Name}: ${products[i].Price}");
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
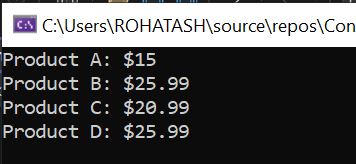
} In this example, the for loop iterates through each element in the products array using an index variable i. For each iteration of the loop, the program displays the name and price of the product. The output of the program would be:
Output
Types of C# Loops
There are three different types of loops in C#.
- While loop
- Do-while loop
- For loop
- ForEach
1. The While loop
A while loop is used to repeat a set of instructions until a specific condition is met. The loop will continue to execute as long as the condition is true.
Syntax of C# While Loop.
while(condition){
//block of code to be executed
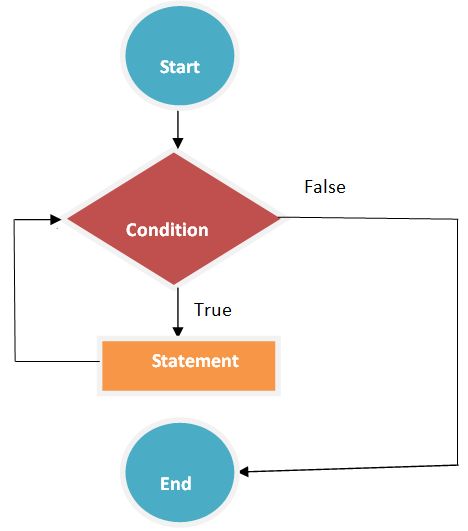
}The following flowchart describes the while loop statement.
Example
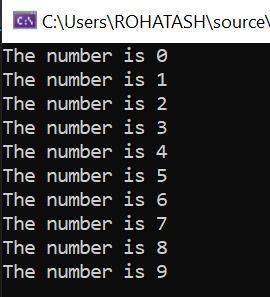
In this example, the while loop will continue to execute as long as count is less than 10. The value of count starts at 0 and increments by 1 each time through the loop. The output of this program would be the numbers 0 through 9 printed to the output window.
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var count = 0;
while (count < 10)
{
Console.WriteLine("The number is " + count + "");
count++;
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}Output
2. The Do-While loop
A do-while loop is similar to a while loop, but the loop will always execute at least once, regardless of whether the condition is true or false. Loops are an essential part of programming, as they allow developers to automate repetitive tasks, iterate over data, and efficiently perform complex operations.
Syntax of C# Do-While Loop as following.
do{
// Code to be executed
}
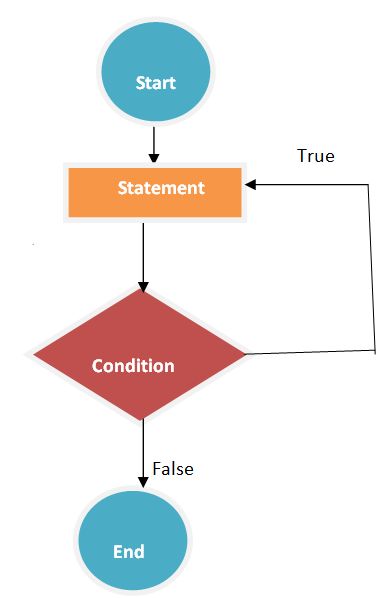
while(condition);The following flowchart describes the do-while loop statement.
Example
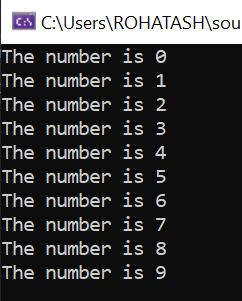
In this example, the do-while loop will execute at least once, printing the number 0 to the browser. The loop will continue to execute as long as count is less than 10, with the value of count incrementing by 1 each time through the loop. The output of this program would be the numbers 0 through 9 printed to the output window.
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var count = 0;
do
{
Console.WriteLine("The number is " + count + "");
count++;
} while (count < 10);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}Output
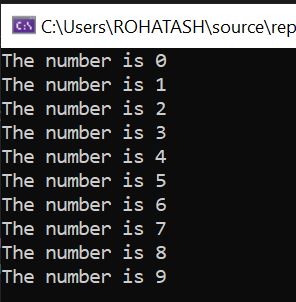
3. The For loop
A for loop is used to iterate a specific number of times. It is commonly used to loop over a collection of data, like an array or a list.
Syntax of C# For Loop as following.
for(initialization; condition; increment) {
// Code to be executed
}The following flowchart describes the For loop statement.
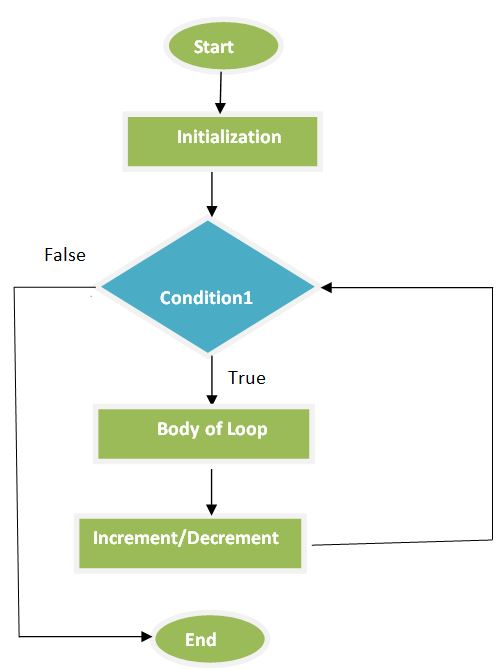
Example
In this example, the for loop will execute 10 times, with the value of count starting at 0 and incrementing by 1 each time through the loop. The output of this program would be the numbers 0 through 9 printed to the output window.
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
for (int count = 0; count < 10; count++)
{
Console.WriteLine("The number is " + count + "");
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}Output
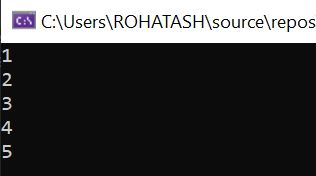
ForEach Loop
The foreach loop is used to iterate over elements in a collection (such as an array or a list). It simplifies iteration by avoiding the need for an index variable.
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] numbers = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
foreach (int number in numbers)
{
Console.WriteLine(number);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}Output
Next
