SQL-Column Joins
SQL Server Joins
In large relational databases, data is stored in tables. Table stored data in columns and rows. Each database has multiple tables. Some large database has hundreds of tables and views. If need data from various tables as application required. You need to query data from these tables based on a related column between them using joins.
Why SQL Joins?
Some time we need to ploating huge number of data from the database. If we store all data in one table its take too much time to load data. So thats why we can fetch data from different table as we need.
Advantage of SQL Joins
SQL Server join is a powerful tool for combining data from two or more tables based on a common column or set of columns. There are several advantages to using SQL Server join, including:
- Efficient data retrieval - SQL Server join allows you to retrieve data from multiple tables with a single query, which can be more efficient than running multiple queries and then combining the results in your application code.
- Simplifies data analysis - Joining tables in SQL Server can simplify data analysis by allowing you to combine related data into a single result set. This makes it easier to perform calculations, create reports, and gain insights into your data.
- Reduces data redundancy - By joining tables in SQL Server, you can avoid duplicating data in multiple tables. This can reduce the amount of storage space required and make it easier to maintain data consistency.
- Provides flexibility - SQL Server join provides a flexible way to combine data from different tables. There are several types of joins available, including inner join, left join, right join, and full outer join, each of which can be used to achieve different results.
- Improves data accuracy - When using SQL Server join, you can ensure that the data you are retrieving is accurate and up-to-date, as the join operation is performed in real-time and updates to one table are automatically reflected in the joined result set.
Disadvantage of SQL Joins
The main disadvantage of joins as following:
- Performance impact - Joining large tables can have a significant impact on query performance. This is especially true if the join involves complex conditions or if the tables being joined have a large number of rows. In some cases, it may be necessary to optimize the database schema or use indexing to improve performance.
- Increased complexity - Joining tables in SQL Server can make queries more complex and harder to write and maintain. It can also make it more difficult to understand the relationships between tables and to troubleshoot issues.
- Data redundancy - While joining tables can reduce data redundancy, it can also lead to data duplication if not done carefully. This can result in larger data storage requirements and increased complexity in maintaining data consistency.
- Potential for errors - Joining tables can introduce the potential for errors, such as incorrect join conditions or incorrect column naming. This can result in inaccurate query results and data inconsistencies.
- Compatibility issues - SQL Server join syntax may not be compatible with other database management systems, which can make it harder to migrate data between systems or integrate with other applications. Joins are not as easy to read as subqueries.
- The maximum number of tables that can be referenced in a single join is 61.
Types of joins in SQL Server
SQL Joins are used to combine data from multiple table. SQL Server mainly supports four types of JOINS, and each join type defines how two tables are related in a query.
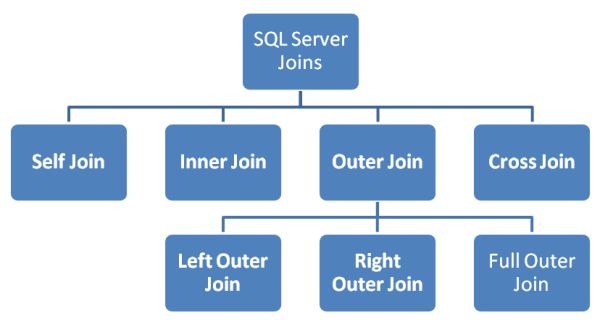
There are four types of joins in SQL Server.
- SELF JOIN - Used to join a table to itself as if the table were two tables, temporarily renaming at least one table in the SQL statement.
- INNER JOIN - Returns rows when there is a match in both tables.
- OUTER JOIN
- Left Outer Join - Returns all rows from the left table, even if there are no matches in the right table.
- Right Outer Join - Returns all rows from the right table, even if there are no matches in the left table.
- Full Outer Join - Returns rows when there is a match in one of the tables.
- Cross Join - Returns the Cartesian product of the sets of records from the two or more joined tables.
Next
