SQL-Sequence
In this article I am going to illustrate how to create and use the Sequence object. To create a sequence of a number in the past, we have used options of IDENTITY. But in SQL Server 2019, there is an interesting option to utilize called Sequence.
SQL Server Sequence
Sequence is a user-defined object that creates a sequence of a number. It has similar functionality to an identity column. You can create it with SQL Server Management Studio or T-SQL.
When to use sequences
You use a sequence object instead of an identity column in the following cases:
- Prior to adding values to the table, the application demands a number.
- The application calls for exchanging a series of numbers between different tables or between different columns of the same database.
- After a certain figure is achieved, the application demands that the number be restarted.
Creating Sequence
The following syntax creates a Sequence object:
CREATE SEQUENCE [schema_name . ] sequence_name
[ AS [ built_in_integer_type | user-defined_integer_type ] ]
[ START WITH ]
[ INCREMENT BY ]
[ { MINVALUE [ ] } | { NO MINVALUE } ]
[ { MAXVALUE [ ] } | { NO MAXVALUE } ]
[ CYCLE | { NO CYCLE } ]
[ { CACHE [ ] } | { NO CACHE } ]
[ ; ] START WITH - Starting number in the sequence
INCREMENT BY
- The incrementing value of the sequence
MINVALUE - The minimum value the sequence can produce.
MAXVALUE - The maximum value the sequence can produce.
CYCLE - If the MAXVALUE is set with the CYCLE, when the MAXVALUE is reached the
sequence will cycle to the MINVALUE and start again.
CACHE - If a CACHE argument is provided, SQL Server will cache (store in memory)
the amount of values specified.
Example
Now let's create a sequence similar to an identity column with 1 as increment.
CREATE SEQUENCE dbo.TestSequence AS BIGINT
START WITH 5
INCREMENT BY 1
MINVALUE 2
MAXVALUE 9
CYCLE
CACHE 10; Now creating a table.
CREATE table TABLEsequenceTest
(
ID INT,
Name nvarchar(100) NOT NULL
) NEXT VALUE FOR
The new NEXT VALUE FOR T-SQL keyword is used to get the next sequential number from a Sequence.
Now insert some data into the table.
INSERT TABLEsequenceTest (ID, Name)VALUES (NEXT VALUE FOR TestSequence, 'Rohatash');
INSERT TABLEsequenceTest (ID, Name)VALUES (NEXT VALUE FOR TestSequence, 'Rahul Kumar');
INSERT TABLEsequenceTest (ID, Name)VALUES (NEXT VALUE FOR TestSequence, 'Ram');
INSERT TABLEsequenceTest (ID, Name)VALUES (NEXT VALUE FOR TestSequence, 'Rohatash');
INSERT TABLEsequenceTest (ID, Name)VALUES (NEXT VALUE FOR TestSequence, 'Rahul');
INSERT TABLEsequenceTest (ID, Name)VALUES (NEXT VALUE FOR TestSequence, 'Ritesh');
INSERT TABLEsequenceTest (ID, Name)VALUES (NEXT VALUE FOR TestSequence, 'Sanjay'); Now use the select statement to see the table data:
SELECT * FROM TABLEsequenceTest The results would look like this:
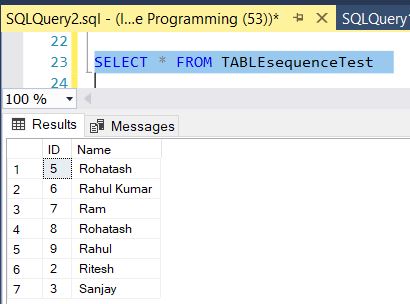
In the preceding image maxvalue is 9. When the MAXVALUE is reached the sequence will cycle to the MINVALUE(2) and start again.
Relate Sequence object to a table
In this example we see how to relate a Sequence object to a table. We have already created a sequence named TestSequence. Now create a new table to define a sequence as an Identity column with the table; see:
CREATE TABLE TABLEsequenceTest2
(
Id INT default (next value for dbo.TestSequence),
Name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL
) Now insert some data into the table:
INSERT TABLEsequenceTest2 (Name)VALUES ('Jimmy');
INSERT TABLEsequenceTest2 (Name)VALUES ('Rahul Kumar');
INSERT TABLEsequenceTest2 (Name)VALUES ('Manish'); Now use a select statement to see the table data:
SELECT * FROM TABLEsequenceTest2 The results would look like this:
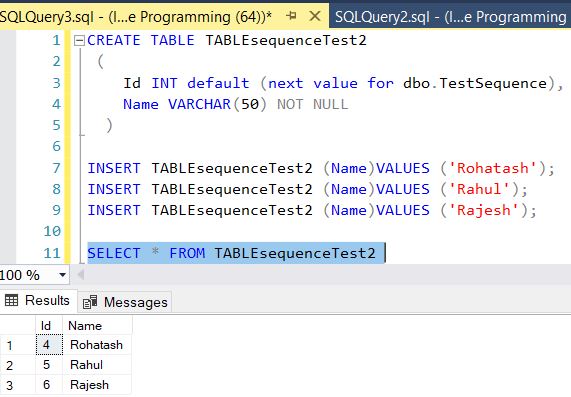
To delete a sequence using Drop keyword
DROP SEQUENCE TestSequence Resetting Sequence using Alter keyword
Argument 'START WITH' cannot be used in an ALTER SEQUENCE statement. Restart with is used in place of start with.
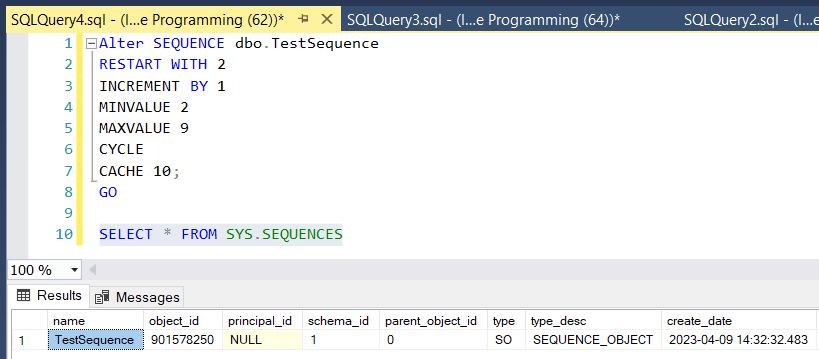
Alter SEQUENCE dbo.TestSequence
RESTART WITH 2
INCREMENT BY 1
MINVALUE 2
MAXVALUE 9
CYCLE
CACHE 10;
GOTo see all sequences available in a database
SELECT * FROM SYS.SEQUENCES Now press F5 to see all the sequences available in a database, as in:
Difference between Sequence and Identity
A Sequence object is similar in function to an identity column. But a big difference is:
- Identity - A value retrieved from an Identity is tied to a specific table column.
- Sequence - A value retrieved from a Sequence object is not tied to a specific table column. That means one Sequence number can be used across multiple tables.
Next
