Angular Architecture
Angular Architecture Overview
Angular is a platform or framework to develop client based applications in HTML and TypeScript. Angular Architecture provides clear guidance on how the application should be structured and offers bi-directional data flow while providing real DOM.
The following diagram shows the architecture of Angular in details.
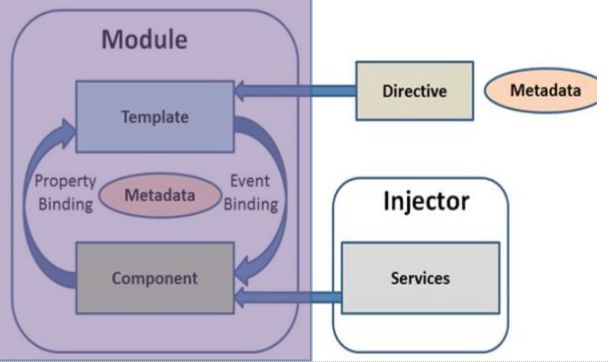
Angular Architecture Overview
The following are the eight building blocks to develop any Angular application.
- Module
- Component
- Metadata
- Template
- Data Binding
- Service
- Directive
- Dependency Injection
1. Module
In Angular, a module is a group or combination of components, directives, pipes and services. An application contains one or more modules every module performs a single task. It help us to keep code clarity and easy to use . At least one module present in every angular application, which is NgModule class. So angular module is the way to share and reuse code across your application or programs.
@NgModule Decorator
The @NgModule decorator is a function ot tag that allows you to create a module that takes a single metadata object whose properties describe the module.By default root module as following:
@NgModule({
declarations: [
AppComponent
],
imports: [
AppRoutingModule,
BrowserModule,
ShareModule,
DashboardModule
],
providers: [],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
export class AppModule { }
The most important array properties are as follow:
- Declarations - The components, pipes, and directives which are belong to NgModule.
- Imports: This property contains the names of other modules whose functionalities are required by the components of this particular module.
- Exports: This property is responsible for making the component template visible to other modules that can import functionalities from this Module.
- Providers: When NgModule runs, its main function which provides the application with services. The provider is responsible for creating Services that the NgModule requires. These services are accessible from all parts of the Application.
- Bootstrap: Thebootstrapoption is like the main() method in other programming language such as c#. This is the Property of Root Module. Bootstrapping is the process which is used to initializes the root module. The root module is responsible for initializing all the other modules when application start.
Types of Angular Modules
Mainly, there are two types of modules in angular. one is Core module and other is Shared module.
- Core Module - The core module is designed for your singleton services shared throughout the application only once. That should only happen in the root or app module of application. So it is imported only once.
- Shared Module - When we reuse components, pipes, and directives. It is called Shared module. Shared will be imported many times in a application.
2. Component
Components are the basic building block of code. a component is a combination of Data, HTML Template and Logic in a view. Components allows re-usability that means we can create component once but we can reused many times within an application and even in other applications. A component can be reused throughout the application and even in other applications. Every angular app has atleast one component. The angular application have more than one components. Each component have small part of UI code. These components works togeather to complete the application. One Angular applications have more then one components. Each component handles a small part of UI functionality. These components work together to produce the complete user interface of the application. The Angular Components are defined using @Component Decorator. This Decorator provides information about the component.
The Components consists of three main building blocks of code.

1. Template - The Templates are nothing but HTML codes along
with the Angular specific HTML markups and directives.
2. Class -
In class which is written in TypeScript. we use to write logic to the View.
Class Contains the Properties & Methods. The Properties of a class can be bind
to the view using Data Binding.
export class AppComponent {
title = 'ComponentDemo';
}@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})The above @Component decorator consists following:
- Selector - It specifies the tag that can be used to call or
render this component in HTML name with
. - TemplateUrl - It is used to indicates the path of the HTML template that will be used to display or render this component.
- StyleUrls - It is used to specifies an array of URLs for CSS style-sheet in the component.
3. Template
The Templates are nothing but HTML codes along with the Angular specific HTML markups and directives.
4. MetaDataA decorator is a function that adds metadata to class, its methods & to its properties. MetaData Provides additional information about the component to the Angular.
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})The above @Component decorator consists following:
- Selector - It specifies the tag that can be used to call or
render this component in HTML name with
. - TemplateUrl - It is used to indicates the path of the HTML template that will be used to display or render this component.
- StyleUrls - It is used to specifies an array of URLs for CSS style-sheet in the component.
5. Data Binding
Every angular component have one class file (.ts file) and a corresponding template file (html file). When work on angular component in application you have to pass data between both template and class file. In this tutorial, we will see how to bind data from class file to template and vice-versa.
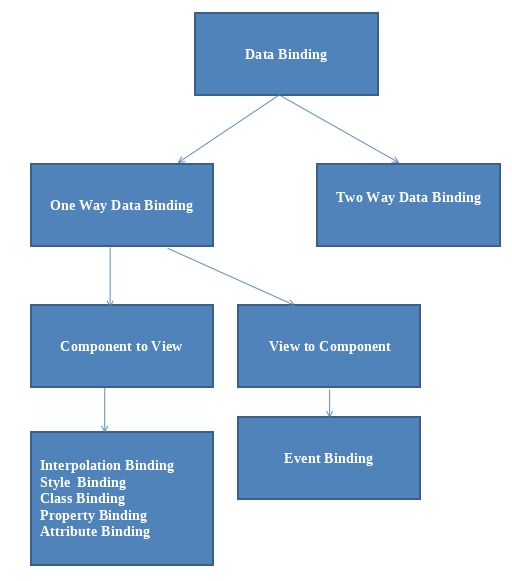
Types of Data Binding in Angular
There are two type of binding in angular. that is called one-way-binding and two-way-binding. The following figure shown bothe type of databinding and also further classification:

1. One Way Data Binding
One-way data binding is a one-way interaction od data between component and its template. If you perform any changes in your component, then it will reflect the HTML elements and vice-versa. You will see following one way data binding:
1. Display data from component to view
- Interpolation or string
- Property
- Class
- Attribute
- Style
2. Display data from view to component
- Event Binding
6. Service
A service is a program that are usually written to perform a specific task or purpose to users. Some common example of service such as file transfer, printing and communication.
Angular Service
When you develop a project many times developers use the same code again and again. In angular also repetitive code in multiple components becomes difficult to manage the code. It will increase the size of the angular project or application. So you need to write such a code which will reusable. To handle that type of situation in angular you can create Services class. In an angular application, the service is responsible for providing the data to the component or specific component task. The following purpose you can use angular service.
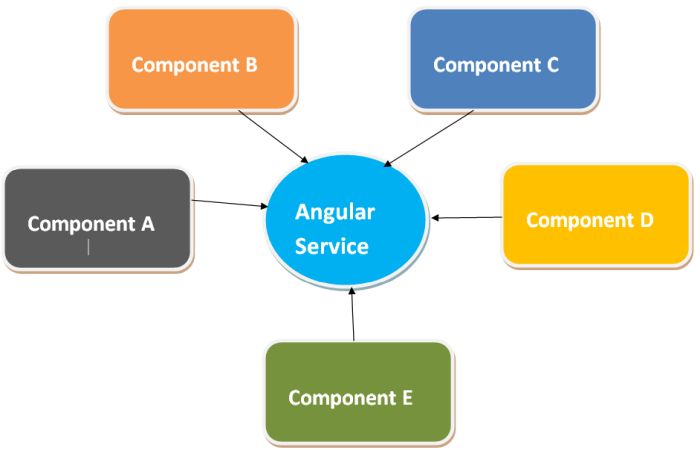
7. Directive
Directives are classes that are used to add additional behavior or modify the existing behavior to the elements in the application. Basically directives are usedto manipulate(adding, removing, updteing) the DOM elements or changing the view of the DOM elements.
Types of Angular
There are Three types of directives in Angular. Angular directives are as follows:
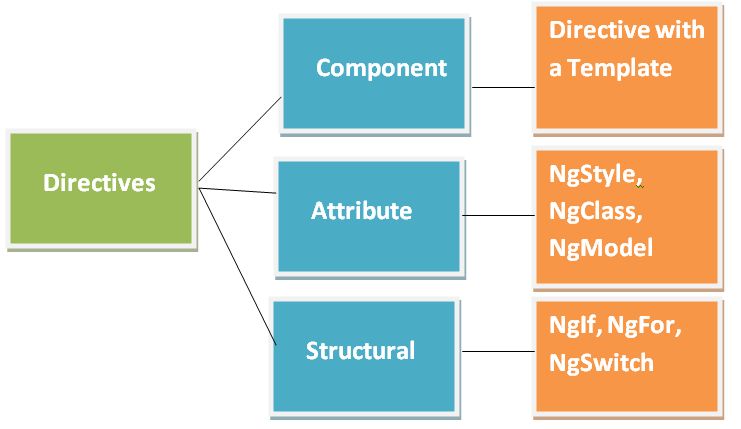
- Components Directives
- Attribute Directives
- Structural Directives
8. Dependency Injection
Dependency Injection is used to make a class independent of its dependencies. Dependency Injection (DI) is a technique in which a class receives its dependencies from outside sources of a class rather than creating them inside class.
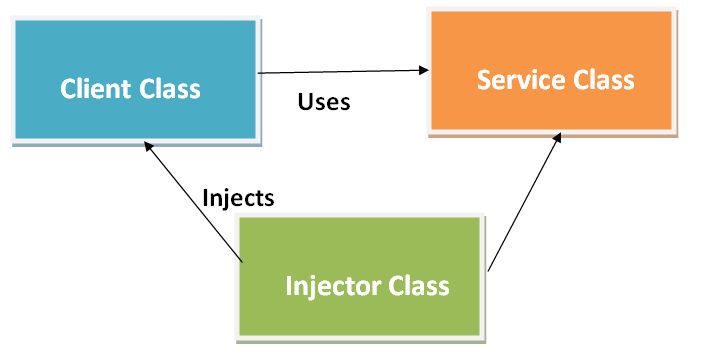
The above image show the following three things:
- Client Class - This is the dependent class which depends on the service class.
- Service Class - This Class is used to provide the service to the client class.
- Injector Class - This class is used to inject the service class object into the client class.
Read more about Dipendency Injection
Prev Next
