LINQ Projection Operators
In LINQ (Language-Integrated Query), projection operators are used to select specific fields from a collection of objects, transforming the objects into a new form. This is typically done using the Select and SelectMany.
There are two types of Projection operators in LINQ.
- Select
- SlectMany
1. Select
The Select operator is used to project each element of a sequence into a new form. It works on a one-to-one basis, meaning each element in the source sequence is transformed into exactly one element in the result sequence.
Example
Suppose we have a list of employees and we want to project their first names and last names.
using System;
using System.Text;
namespace FirstProgram
{
public class Employee
{
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var employees = new List<Employee>
{
new Employee { FirstName = "Rohatash", LastName = "Kumar", Age = 35 },
new Employee { FirstName = "Mohit", LastName = "Kumar", Age = 32 },
new Employee { FirstName = "Saurav", LastName = "Kumar", Age = 34 }
};
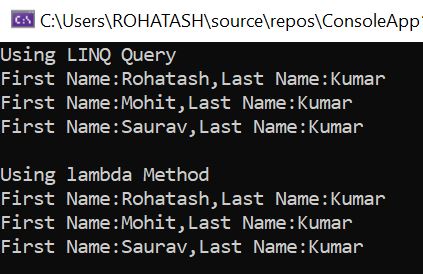
// Using LINQ
Console.WriteLine("Using LINQ Query");
var result = from p in employees
select new{FirstName = p.FirstName, LastName = p.LastName};
foreach (var employee in result)
{
Console.WriteLine("First Name:" + employee.FirstName + ",Last Name:" + employee.LastName);
}
// Using lambda
Console.WriteLine("");
Console.WriteLine("Using lambda Method");
var projectedData = employees.Select(e => new { e.FirstName, e.LastName });
foreach (var employee1 in projectedData)
{
Console.WriteLine("First Name:" + employee1.FirstName+",Last Name:"+ employee1.LastName);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}Output
2. SelectMany
The SelectMany operator is used to project each element of a sequence into a new form and then flatten the resulting sequences into one sequence. It works on a one-to-many basis, meaning each element in the source sequence can be transformed into zero or more elements in the result sequence.
Example
Suppose we have a list of departments, each with a list of employees, and we want to project all employees into a single flat list.
using System;
using System.Text;
namespace FirstProgram
{
public class Department
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public List Employees { get; set; }
}
public class Employee
{
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var departments = new List
{
new Department { Name = "HR", Employees = new List<Employee> { new Employee { FirstName = "Rohatash", LastName = "Kumar", Age = 35 } } },
new Department { Name = "IT", Employees = new List<Employee> { new Employee { FirstName = "Mohit", LastName = "Kumar", Age = 32 } } },
new Department { Name = "IT", Employees = new List<Employee> { new Employee { FirstName = "Saurav", LastName = "Kumar", Age = 34 } } }
};
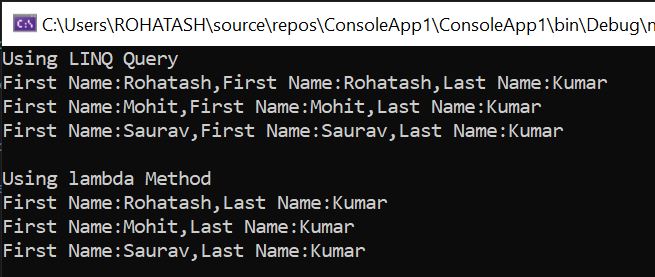
// Using LINQ
Console.WriteLine("Using LINQ Query");
var allEmployees = from d in departments
from e in d.Employees
select e;
foreach (var employee in allEmployees)
{
Console.WriteLine("First Name:" + employee.FirstName + ",First Name:" + employee.FirstName + ",Last Name:" + employee.LastName);
}
// Using lambda
Console.WriteLine("");
Console.WriteLine("Using lambda Method");
var allEmployees1 = departments.SelectMany(d => d.Employees);
foreach (var employee1 in allEmployees1)
{
Console.WriteLine("First Name:" + employee1.FirstName+",Last Name:"+ employee1.LastName);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
} Output
Key Differences
-
Projection Type
- Select is used for a simple projection where each element in the source sequence maps to exactly one element in the result sequence.
- SelectMany is used when each element in the source sequence can map to multiple elements in the result sequence, and the results need to be flattened into a single sequence.
-
Flattening
- Select does not flatten sequences; it maintains the hierarchy of the source sequence.
- SelectMany flattens the sequences, resulting in a single, flat sequence of elements.
-
Use Case
- Use Select when you need to transform elements directly without changing the structure of the sequence.
- Use SelectMany when you need to transform elements that result in nested sequences and you want a flat result.
Prev Next
