LINQ Partitioning operators
Partitioning operators in LINQ are used to divide a sequence into two parts and then return one of the parts. Common partitioning operators in LINQ include Take, Skip, TakeWhile, and SkipWhile.
- Take
- Skip
- TakeWhile
- SkipWhile
1. Take Operator
The Take operator returns a specified number of contiguous elements from the start of a sequence.
Example
using System;
namespace FirstProgram
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
List<int> numbers = new List<int> { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 };
// Using Take to get the first 3 numbers
var firstThreeNumbers = numbers.Take(3);
foreach (var num in firstThreeNumbers)
{
Console.WriteLine(num); // Output: 1, 2, 3
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}Output

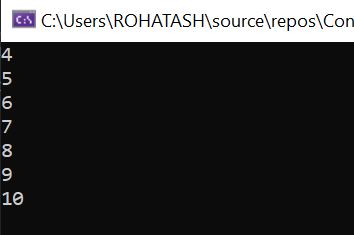
2. Skip Operator
The Skip operator bypasses a specified number of elements in a sequence and then returns the remaining elements.
Example
using System;
namespace FirstProgram
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
List<int> numbers = new List<int> { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 };
// Using Skip to bypass the first 3 numbers
var allButFirstThreeNumbers = numbers.Skip(3);
foreach (var num in allButFirstThreeNumbers)
{
Console.WriteLine(num); // Output: 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}Output
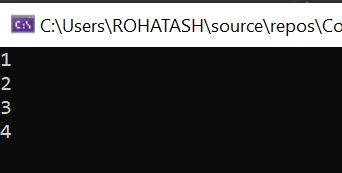
3. TakeWhile Operator
The TakeWhile operator returns elements from a sequence as long as a specified condition is true. Once the condition is false, the operator stops and returns the elements collected so far.
Example
using System;
namespace FirstProgram
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
List<int> numbers = new List<int> { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 };
// Using TakeWhile to get numbers less than 5
var numbersLessThanFive = numbers.TakeWhile(n => n < 5);
foreach (var num in numbersLessThanFive)
{
Console.WriteLine(num); // Output: 1, 2, 3, 4
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}Output
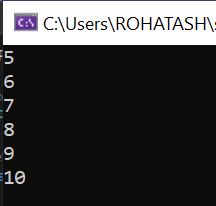
4. SkipWhile Operators
The SkipWhile operator in LINQ bypasses elements in a sequence as long as a specified condition is true and then returns the remaining elements. It is useful when you want to ignore a portion of a sequence based on a condition and work with the rest.
Example
Consider a list of integers. We want to skip elements in the list as long as the element is less than 5.
using System;
namespace FirstProgram
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
List<int> numbers = new List<int> { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 };
// Using SkipWhile to skip numbers less than 5
var numbersStartingFromFive = numbers.SkipWhile(n => n < 5);
foreach (var num in numbersStartingFromFive)
{
Console.WriteLine(num); // Output: 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}Output
In this example, SkipWhile processes the list and skips elements as long as the condition n < 5 is true. When it encounters the number 5, which does not satisfy the condition, it stops skipping and starts returning the remaining elements.
Prev Next
