`
MVC-Routing
Routing in MVC (Model-View-Controller) is the process of mapping incoming requests to the appropriate controller and action method.
Advantages of Routing
- Clean and SEO-Friendly URLs - Users see meaningful URLs like /Products/Details/1 instead of query strings.
- Flexibility - Developers can define custom routes for different scenarios.
- Extensibility - Supports complex route patterns with constraints.
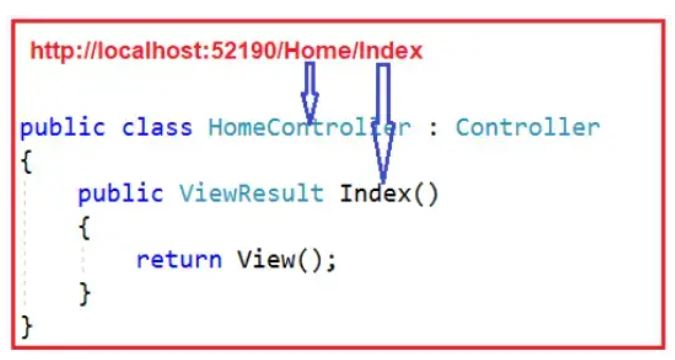
How Routing Works
- Request URL - The user enters a URL in the browser.
- Route Matching - The routing engine matches the URL against the defined routes in the RouteConfig file (or endpoint routing in newer frameworks like ASP.NET Core).
- Controller and Action Selection - Once a match is found, the request is routed to the corresponding controller and action method.
- Execution - The action method processes the request and returns the appropriate result, such as an HTML page or JSON data.
Types of Routing
There are two types routing in MVC.
- Convention-Based Routing (Classic Routing)
- Attribute Routing
1. Convention-Based Routing (Classic Routing)
Routes are defined in RouteConfig or Startup.
Example
routes.MapRoute(
name: "ProductRoute",
url: "Products/{category}/{id}",
defaults: new { controller = "Products", action = "Details", id = UrlParameter.Optional }
);2. Attribute Routing
Routes are defined directly in controllers using attributes.
Example
[Route("Products/Details/{id}")]
public ActionResult Details(int id)
{
// Your code here
}Next
