ReactJS Virtual DOM
In this tutorial we will see the most important feature Virtual DOM of ReactJs. Before understading that we will learn about basic DOM and how it works in traditional webpages. To make DOM better, React brought into the scene the virtual DOM.
What is DOM?
When we use simple HTML to create a Web page. Normally we use JavaScript to interact with the traditional HTML markup. This is where DOM or Document Object Model comes in.
- DOM stands for Document Object Model.
- It is a World Wide Web Consortium(W3C) standard logical representation of any webpage.
- It represents the entire UI(User Interface) of the web application as the tree data structure.
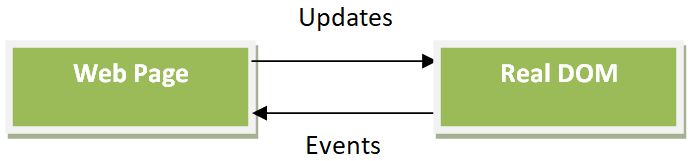
- It's the interface between JavaScript and the web browser. With the help of the DOM.
- When a web page is loaded on the browser creates a Document Object Model of the page.
- DOM is a tree-like structure that contains all the elements and it’s properties of a website as its nodes.
- It is a platform and language-neutral interface that allows programs to dynamically access and update the content, structure, and style of a document.
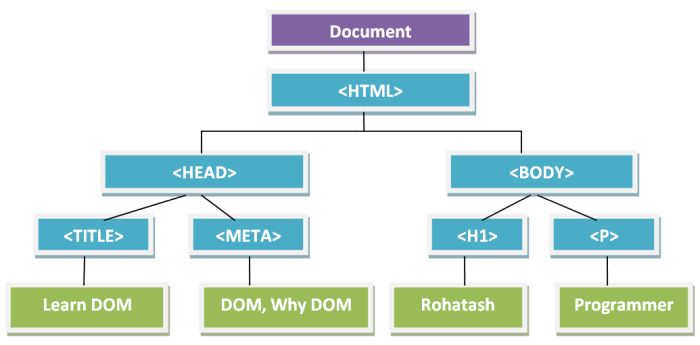
HTML DOM Representation
When a web page is loaded, the browser creates a Document Object Model of the page.
The elements in the tree now are treated as objects not traditional HTML tags. These objects are now identified using their id which can be thought to be a reference (similar to pointers). So, now JavaScript etc can easily know what elements are there in the code, what are their properties and their location. They can now be manipulated as objects and easily modified. This modification is called working with the DOM.
In the Above DOM, JavaScript gets all the power it needs to create dynamic HTML.
- JavaScript can change all the HTML elements in the page
- JavaScript can change all the HTML attributes in the page
- JavaScript can change all the CSS styles in the page
- JavaScript can remove existing HTML elements and attributes
- JavaScript can add new HTML elements and attributes
For Example
To find an HTML element in the DOM, is by using the element id method to modify the contents of DOM. Whenever there is any change that occurs in the state of your application, the DOM is updated to reflect the change in the UI.
var elementid = document.getElementById("id");
Using the above id we can update html element.
Creating Element in DOM
The following code show how we can add elements in DOM.
for (var i=0; i<10000; i++) {
$("BODY").append($("<div />"));
}
So in the above example each time elements will be added to the DOM. So every time DOM will also reload.
Problem with HTML DOM
Whenever each time an update in the state of the application UI by developer, The DOM is rendered and manipulated with every change which made the total process to consume a lot of time. So it make application slow. As a betterment, React brought into the scene the virtual DOM. The Virtual DOM can be referred to as a copy of the actual DOM representation that is used to hold the updates made by the user and finally reflect it over to the original Browser DOM at once consuming much lesser time.
Virtual DOM in ReactJS
It is a replica or copy of the real DOM. Whenever any component changes due to user input, this change is reflected in the Virtual DOM. The virtual DOM then compare with the real DOM, and only the changed component is updated. Hence instead of changing the whole DOM, only a specific part is changed. It results in fast application rendering.
The following points define the Virual DOM better way.
- Virtual DOM is the virtual representation of Real DOM.
- It is an in-memory replica of the actual DOM.
- Virtual DOM is just an object representing the UI. Nothing gets drawn on the screen.
- Virtual DOM is just like a blueprint of Machine. When you make any change in the bluprint but those changes will not directly apply to the machine.
- React update the state changes in Virtual DOM first and then it syncs with Real DOM.
- Virtual DOM is a programming concept where a virtual representation of a UI is kept in memory synced with Real DOM by a library such as ReactDOM and this process is called reconciliation.
- Virtual DOM makes the performance faster of web application. The reason is the amount of changed information rather than wasting time on updating the entire page.
- It improves performance and is the main reason developers love ReactJS and its Virtual DOM.
- It is Used by libraries or frameworks like React.js, Vue.js etc.
How Virtual DOM Works in ReactJS?
The image below shows the virtual DOM tree and the diffing process.
- Every UI consists of distinct components, and each component has its own state.
- ReactJS tracks state changes and adheres to observable patterns.
- ReactJS refreshes the virtual DOM tree but does not alter the real DOM tree whenever the state of the component is altered in any way.
- After updating, ReactJS compares the virtual DOM's present and prior version.
- React is aware of which virtual DOM objects have changed. The actual DOM objects are replaced, necessitating little manipulation actions.
- This process is called differentiation. This picture will make the concept clear.

The nodes that have changed are shown as red circles. The UI elements whose status has changed are represented by these nodes. The difference between the previous version of the virtual DOM tree and the current virtual DOM tree is then calculated. To provide the new UI, the entire parent subtree is then re-rendered. This updated tree is then batch updated to the real DOM.
Let us look at a sample code to see what it looks like:
Initial DOM State
<div>
<div>
<h1>Hello Gaurav</h1>
</div>
<div>
<h1>Hello Rohatash</h1>
</div>
</div>Update DOM State
<div>
<div>
<h1>Hello Gaurav</h1>
</div>
<div>
<h1>Hello Rahul </h1>
</div>
</div>When the DOM receives an update, it changes only the content of the DOM as we can find in the second block of code. This update is so fast that we don’t usually know when this happens. It only marks the component which needs to be updated and updates it for us.
Prev Next
