Versioning in .NetCore
Versioning Introduction
Versioning in ASP.NET Core Web API allows you to introduce new API versions without breaking existing clients. This is crucial for maintaining backward compatibility and smooth upgrades. Here’s a detailed look at the steps to implement versioning in ASP.NET Core Web API and why it's beneficial.
Why Use Versioning
- Backward Compatibility - Ensures existing clients using older versions of your API continue to work even after new versions are introduced.
- Smooth Transition - Allows gradual transition to newer API versions, giving clients time to adapt.
- Better Client Management - Helps manage different clients using different API versions.
-
Clear API Evolution - Tracks the changes and evolution of your API over time.
Implementing Versioning in ASP.NET Core 7 and 8
-
Install the Versioning Package
First, install the Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.Versioning package. This can be done via NuGet Package Manager or by running the following command.
dotnet add package Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.Versioning -
Configure Services in Startup.cs or Program.cs: Depending on your project structure, you will add API versioning in either Startup.cs or Program.cs. Since ASP.NET Core 6 and later uses Program.cs for minimal hosting, I'll show both ways.
In Startup.cs
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) { services.AddControllers(); services.AddApiVersioning(options => { options.DefaultApiVersion = new ApiVersion(1, 0); options.AssumeDefaultVersionWhenUnspecified = true; options.ReportApiVersions = true; options.ApiVersionReader = new UrlSegmentApiVersionReader(); }); }In Program.cs
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args); builder.Services.AddControllers(); builder.Services.AddApiVersioning(options => { options.DefaultApiVersion = new ApiVersion(1, 0); options.AssumeDefaultVersionWhenUnspecified = true; options.ReportApiVersions = true; options.ApiVersionReader = new UrlSegmentApiVersionReader(); }); var app = builder.Build(); app.UseHttpsRedirection(); app.UseAuthorization(); app.MapControllers(); app.Run(); Define API Versions in Controllers - Annotate your controllers with API version attributes to specify the versions. By using versioning, you can ensure the longevity and evolution of your API without disrupting existing clients.
[ApiController] [Route("api/v{version:apiVersion}/[controller]")] [ApiVersion("1.0")] public class SampleControllerV1 : ControllerBase { [HttpGet] public IActionResult GetV1() { return Ok("This is version 1.0"); } } [ApiController] [Route("api/v{version:apiVersion}/[controller]")] [ApiVersion("2.0")] public class SampleControllerV2 : ControllerBase { [HttpGet] public IActionResult GetV2() { return Ok("This is version 2.0"); } }-
Versioning Schemes - Different methods to version your API include.
- URL Path Versioning - e.g., api/v1/resource.
- Query String Versioning - e.g., api/resource?api-version=1.0.
- Header Versioning - e.g., api/resource with api-version: 1.0.
- Media Type Versioning - e.g., Accept: application/json;v=1.0.
Configure different version readers as shown.
builder.Services.AddApiVersioning(options => { options.ApiVersionReader = new QueryStringApiVersionReader("api-version"); // For query string versioning // options.ApiVersionReader = new HeaderApiVersionReader("api-version"); // For header versioning // options.ApiVersionReader = new MediaTypeApiVersionReader(); // For media type versioning });
Versioning Types in an .NET Core Web API
The below are the following types of versioning.
- URL Path Versioning
- Query String Versioning
- Header Versioning
- Media Type Versioning
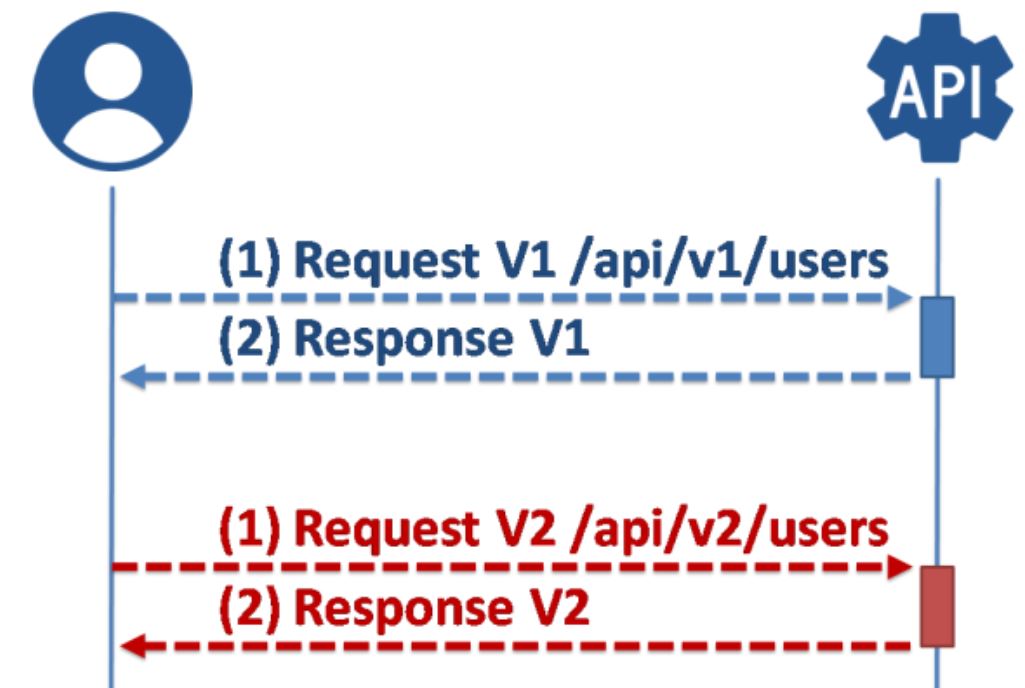
1. URL Path Versioning
URL Path Versioning includes the version number in the URL path. This is one of the most common and straightforward ways to version an API.
Example
[ApiController]
[Route("api/v{version:apiVersion}/products")]
[ApiVersion("1.0")]
public class ProductsV1Controller : ControllerBase
{
[HttpGet]
public IActionResult GetV1()
{
return Ok("This is products version 1.0");
}
}
[ApiController]
[Route("api/v{version:apiVersion}/products")]
[ApiVersion("2.0")]
public class ProductsV2Controller : ControllerBase
{
[HttpGet]
public IActionResult GetV2()
{
return Ok("This is products version 2.0");
}
}Request Examples
-
GET /api/v1/products -
GET /api/v2/products
2. Query String Versioning
Query String Versioning uses a query parameter to specify the API version.
Example
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddControllers();
services.AddApiVersioning(options =>
{
options.ApiVersionReader = new QueryStringApiVersionReader("api-version");
});
}
[ApiController]
[Route("api/products")]
[ApiVersion("1.0")]
public class ProductsV1Controller : ControllerBase
{
[HttpGet]
public IActionResult GetV1()
{
return Ok("This is products version 1.0");
}
}
[ApiController]
[Route("api/products")]
[ApiVersion("2.0")]
public class ProductsV2Controller : ControllerBase
{
[HttpGet]
public IActionResult GetV2()
{
return Ok("This is products version 2.0");
}
}Request Examples
-
GET /api/products?api-version=1.0 -
GET /api/products?api-version=2.0
3. Header Versioning
Header Versioning uses a custom header to specify the API version.
Example
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddControllers();
services.AddApiVersioning(options =>
{
options.ApiVersionReader = new HeaderApiVersionReader("api-version");
});
}
[ApiController]
[Route("api/products")]
[ApiVersion("1.0")]
public class ProductsV1Controller : ControllerBase
{
[HttpGet]
public IActionResult GetV1()
{
return Ok("This is products version 1.0");
}
}
[ApiController]
[Route("api/products")]
[ApiVersion("2.0")]
public class ProductsV2Controller : ControllerBase
{
[HttpGet]
public IActionResult GetV2()
{
return Ok("This is products version 2.0");
}
}Request Examples
-
GET /api/productswith headerapi-version: 1.0 -
GET /api/productswith headerapi-version: 2.0
4. Media Type Versioning
Media Type Versioning uses the media type of the request to specify the API version.
Example
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddControllers();
services.AddApiVersioning(options =>
{
options.ApiVersionReader = new MediaTypeApiVersionReader();
});
}
[ApiController]
[Route("api/products")]
[ApiVersion("1.0")]
public class ProductsV1Controller : ControllerBase
{
[HttpGet]
public IActionResult GetV1()
{
return Ok("This is products version 1.0");
}
}
[ApiController]
[Route("api/products")]
[ApiVersion("2.0")]
public class ProductsV2Controller : ControllerBase
{
[HttpGet]
public IActionResult GetV2()
{
return Ok("This is products version 2.0");
}
}Request Examples
-
GET /api/productswith headerAccept: application/json;v=1.0 -
GET /api/productswith headerAccept: application/json;v=2.0
Prev Next
