Routing in .NetCore
Routing in ASP.NET Core is the process of matching incoming HTTP requests to appropriate endpoints (such as controllers or Razor pages) based on URL patterns. Routing plays a crucial role in how requests are processed and helps build clean and organized APIs or web applications. Let's dive into the details.
1. What is Routing?
Routing is the mechanism in ASP.NET Core that maps the incoming request's URL to a specific action in a controller or a Razor page. When a request is made to the application, the routing system examines the URL and attempts to match it with a predefined route template to invoke the corresponding logic.
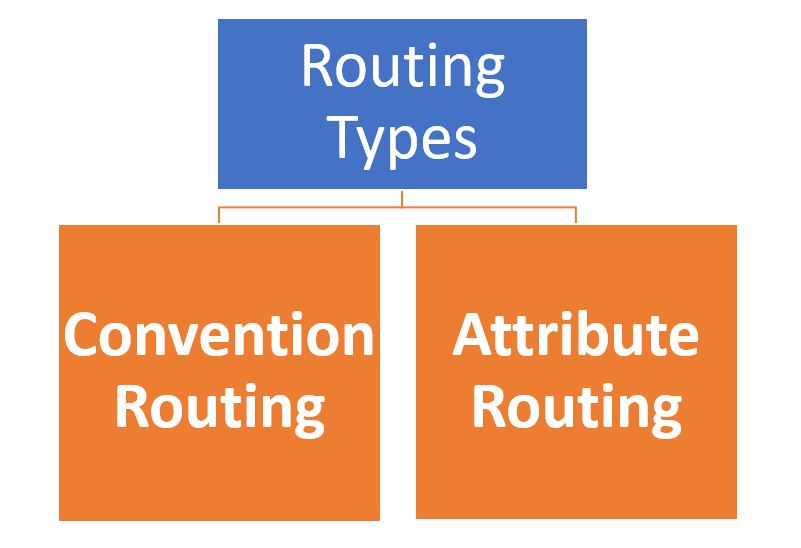
2. Types of Routing
There are two main types of routing in ASP.NET Core:
- Convention-based Routing (used primarily in MVC applications)
- Attribute-based Routing (explicitly specified at the controller or action level)
1. Convention-based Routing
In convention-based routing, routes are configured centrally in the program.cs file. This is typically used for organizing routes in MVC applications.
Example
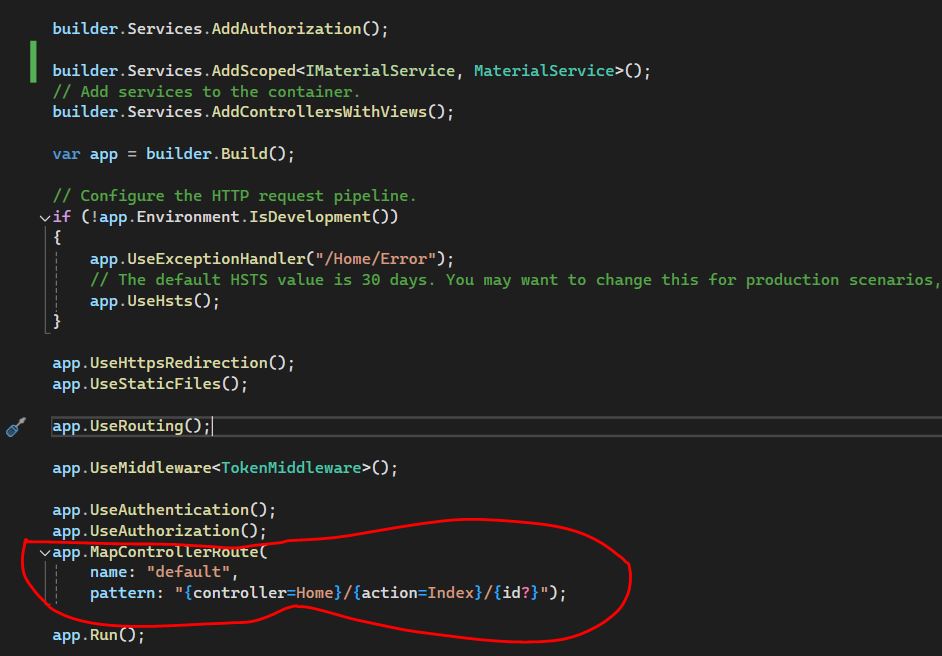
In this example, the URL pattern "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}" tells the application that:
- The controller part of the URL should be mapped to a controller class (e.g., HomeController).
- The action part should map to a method (e.g., Index()).
- The id is optional (id?), allowing it to be omitted from the URL.
URL Example
A URL like /Product/Details/3 would map to the ProductController's Details method, with id = 3.
2. Attribute-based Routing
With attribute routing, the routes are specified directly on the controller or action methods using attributes like [Route], [HttpGet], [HttpPost] etc.
Example
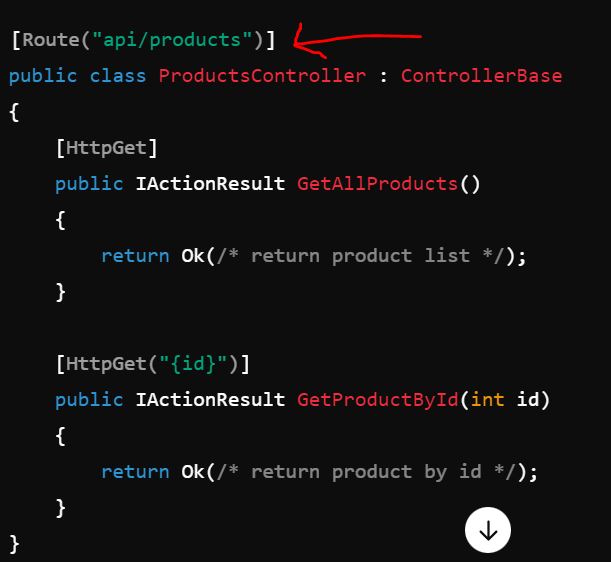
In this example
- /api/products invokes the GetAllProducts method.
- /api/products/5 invokes the GetProductById method and passes id = 5 to the method.
Advanced Routing Features
ASP.NET Core routing provides various advanced features for handling complex routing scenarios.
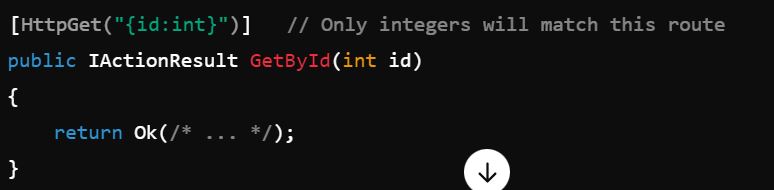
1. Route Constraints
You can impose restrictions on parameters by using route constraints, ensuring that only certain values match a route.
Example
2. Optional Parameters
In routing templates, parameters can be marked as optional by appending ? to them.
Example
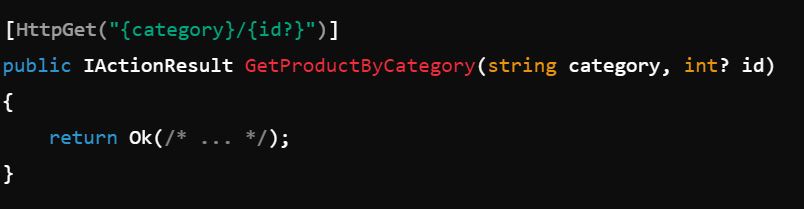
3. Default Values
You can set default values for parameters in the routing template.
Example
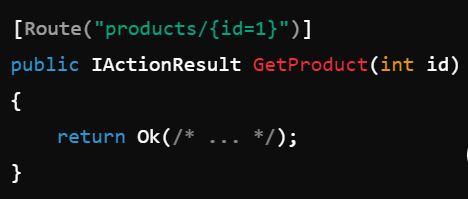
Here, if the id is not provided, it defaults to 1.
Prev Next
