Cloud Computing - Deployment Models
Cloud deployment models describe how cloud computing resources and services are hosted, managed, and made available to users and organizations. It simply refers to delivering computing resources, such as servers, storage, databases, software, and applications, over the Internet.
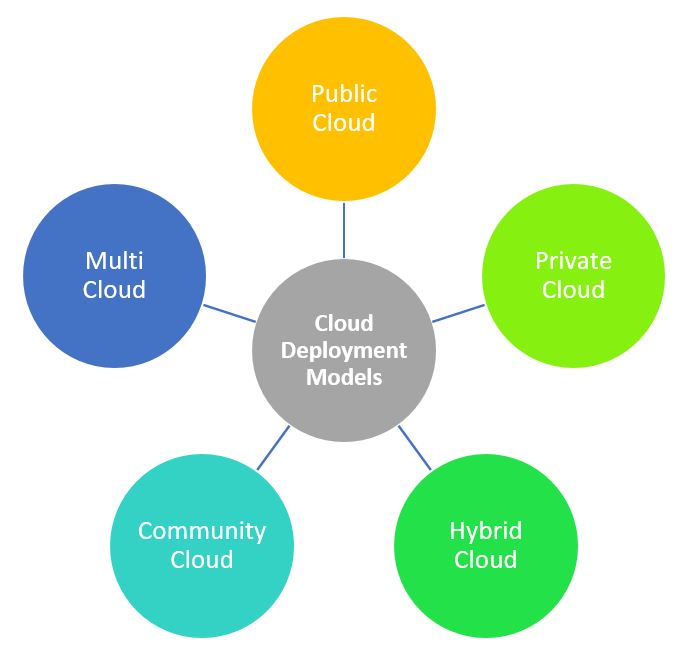
Types of Cloud Deployment Models
There are several deployment models, each with its own characteristics and use cases. The main cloud deployment models are as following:
- Public Cloud
- Private Cloud
- Hybrid Cloud
- Community Cloud
- Multi Cloud
1. Public Cloud
In public cloud, computing resources are managed and operated by the Cloud Service Provider (CSP). These providers make their infrastructure and services available to the general public over the internet. The public cloud provider supplies the infrastructure needed to host and deploy workloads in the cloud. It also offers tools and services to help customers manage cloud applications, such as data storage, security and various monitoring and reporting capabilities. The IT giants such as Google, Amazon and Microsoft offer cloud services via Internet.
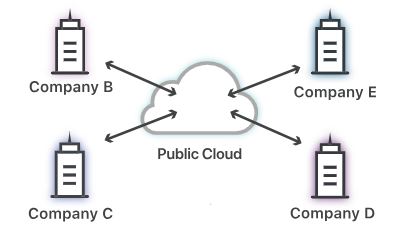
A common public cloud example is to think of it as similar to renting an apartment:
- You pay rent for a single unit
- The building manager handles the maintenance
- You share the overall space with other tenants, with security around your own belongings
How Public Cloud Work?
Using any number of virtual machines (VMs), which are divided from big collections of third-party-owned data centers, IT administrators can build a public cloud network. Third-party providers can provide end users with a variety of cloud services, from basic storage options to software programs and development tools—all accessible with an Internet connection—by virtualizing their compute, processing, and storage capabilities. These services are accessible to end customers from numerous organizations via mobile applications or other web portals.
Public cloud is owned, managed, and operated by businesses, universities, government organizations, or a combination of them.
For their services, third parties frequently demand a fixed or pay-per-use price. In exchange, the provider of public clouds takes over daily IT administration, including public cloud security. Google, Microsoft, Dropbox, and many other companies are examples of public cloud service providers.
Advantages of Public Cloud
There are the following advantages of public cloud.
- Low Cost - Public cloud has a lower cost than private, or hybrid cloud, as it shares the same resources with a large number of consumers.
- Location Independent - Public cloud is location independent because its services are offered through the internet.
- Save Time - In the public cloud, the cloud service provider is in charge of managing and maintaining the data centers where data is stored, allowing users to save time when configuring and assembling servers, establishing connectivity, deploying new products, and so on.
- Quickly and easily set up - Public cloud services are simple for businesses to purchase online, deploy, and configure remotely through the cloud service provider in a matter of hours.
- Business Agility - The public cloud offers the capability to elastically resize computer resources in accordance with the needs of the enterprise.
- Scalability and Reliability - Public cloud offers scalable (easy to add and remove) and reliable (24*7 available) services to the users at an affordable cost.
Disadvantages of Public Cloud
Public cloud have following disadvantage also.
- Low Security - Public Cloud is less secure because resources are shared publicly or any one can use.
- Performance - In the public cloud, performance depends upon the speed of internet connectivity.
- Less customizable - Public cloud is less customizable than the private cloud.
2. Private Cloud
Private cloud is also known as an internal cloud or corporate cloud. A private cloud is a cloud service that is not shared with any other organization. The private cloud user has the cloud to themselves.
Private cloud provides computing services to a private internal network (within the organization) and selected users instead of the general public.
Private cloud provides a high level of security and privacy to data through firewalls and internal hosting. It also ensures that operational and sensitive data are not accessible to third-party providers.
HP Data Centers, Microsoft, Elastra-private cloud, and Ubuntu are the example of a private cloud.
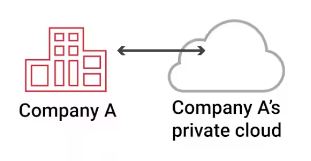
A Common Private Cloud Example
Private cloud is more like owning a house, where you have your own personal space that belongs to you, but you’re also personally responsible for the overall care and upkeep. However, there are cases where a business may choose a private cloud to fulfill certain requirements, such as industry or region-specific compliance and data sovereignty needs.
How Private Cloud Works?
A single-tenant environment, a private cloud prevents businesses from sharing
their resources with other users or clients. There are numerous ways to host and
manage these materials. The infrastructure and resources already available in
the company's on-site data center may be used to build the Private Cloud in some
cases. If not, new infrastructure can be created independently with the aid of a
third party provider.
But there are some circumstances in which the single-tenant environment is being
tested independently by using virtualization software. However, the private
Cloud and its resources are devoted to a single tenant or user. One of the cloud
deployment models is the private cloud. All three types of clouds - public,
private, and hybrid - share key cloud infrastructure elements.
Advantages of Private Cloud
There are the following advantages of private cloud.
- More Control - The private Cloud offers more control over the resources and hardware than the public Cloud. This is because only authorized users have access.
- Security and Privacy - The main advantage of the Private Cloud is its security and privacy. It consists of improved and additional security levels compared to Public Cloud.
- Improved Performance - Users adopting Private Cloud experience better performance with improved speed and space.
- Customization - Private Cloud offers a complete configuration to the organization. A private cloud is built under the guidance of an experienced on-site cloud architect, which means organizations can specify the exact required environment to run applications. Hosted Private cloud is beneficial, and there is no requirement for on-premises setup. In this scenario, the business and vendor will work together to design and manage the Cloud.
- Hybrid Integration - Sometimes an application requires additional computing resources. In this case, hybridization helps extend the private Cloud resources into a public cloud to maintain uptime without installing additional servers. It can be a cost-effective solution for businesses who require a private Cloud security level and want to function as a public cloud.
Disadvantages of Private Cloud
Private cloud have following disadvantage also.
- High Cost - Private Cloud is costlier than Public Cloud as the setup cost, and maintenance cost are expensive.
- The restricted area of Operations - In a Private Cloud, the operations are finite within an organization, so the functions are finite.
- Limited Scalability - Scaling in Private Cloud can be hosted within the internal resources capacity of an organization.
- Skilled People - Skilled People are significant for an organization to manage and operate cloud services.
- Up-Front Cost - Fully Private Clouds are hosted on-site and require heavy capital. In a Private Cloud, the hardware requirements can be costly, and an expert cloud architect is necessary for setting up, maintaining, and managing the environment.
- Capacity Utilization - Organization is responsible for maximizing the utilization capacity in Private Cloud.
Top Private Cloud Providers
Below is the list of top and leading Private Cloud Providers, and they are as follows:
- Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE)
- Cisco
- Microsoft
- VMware
- Dell EMC
- Oracle
- IBM
- Red Hat
3. Hybrid Cloud
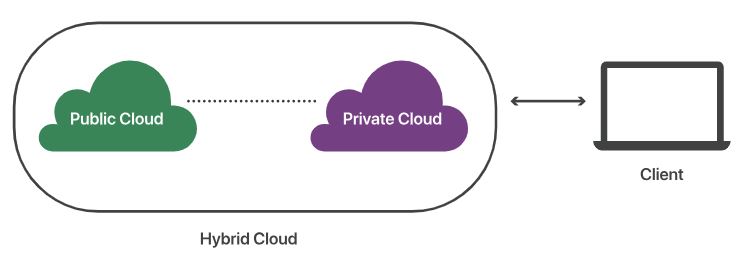
Hybrid cloud is a computing environment that combines elements of both public and private clouds, allowing data and applications to be shared between them.
Hybrid cloud = public cloud + private cloud
a hybrid cloud is used in finance, healthcare, and Universities. The best hybrid cloud provider companies are Amazon, Microsoft, Google, Cisco, and NetApp.
Advantages of Hybrid Cloud
Here are some key characteristics and aspects of hybrid cloud.
- Public Cloud - This is a cloud computing model where services and resources are provided by third-party cloud service providers and are accessible over the internet. Public clouds are often used for scalable and cost-effective storage and compute resources.
- Private Cloud - A private cloud is typically hosted within an organization's own data centers or on dedicated infrastructure. It offers greater control, security, and customization but can be more expensive to set up and maintain.
- Integration - The key feature of a hybrid cloud is the integration between public and private clouds. This integration is facilitated by a combination of technologies, such as virtual private networks (VPNs), dedicated connections, and hybrid cloud management platforms.
- Data and Application Portability - In a hybrid cloud, data and applications can move between the public and private clouds seamlessly. This allows organizations to take advantage of the scalability of the public cloud while keeping sensitive or critical workloads in a private cloud for added security.
- Resource Optimization - Hybrid cloud allows organizations to optimize their IT resources. They can use public cloud resources to handle spikes in demand while maintaining a private cloud for steady-state workloads.
- Security and Compliance - Hybrid cloud deployments can be tailored to meet specific security and compliance requirements. Sensitive data can be stored and processed in the private cloud, while less sensitive data can reside in the public cloud.
- Cost Management - Organizations can achieve cost savings by using public cloud resources only when needed and relying on private cloud resources for predictable workloads. This cost flexibility is often referred to as "cloud bursting."
- Disaster Recovery - Hybrid cloud provides an effective disaster recovery solution. Data and applications can be replicated to the public cloud for backup and recovery purposes, ensuring business continuity in case of a disaster.
- Flexibility - Organizations have the flexibility to choose the right cloud model for each application or workload, depending on factors like performance, scalability, and security requirements.
Disadvantages of Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid cloud have following disadvantage also.
- Networking issues - In the Hybrid Cloud, networking becomes complex because of the private and the public cloud.
- Infrastructure Compatibility - Infrastructure compatibility is the major issue in a hybrid cloud. With dual-levels of infrastructure, a private cloud controls the company, and a public cloud does not, so there is a possibility that they are running in separate stacks.
- Reliability - The reliability of the services depends on cloud service providers.
4. Community Cloud
Community cloud computing refers to a shared cloud computing service environment that is targeted to a limited set of organizations or employees (such as banks or heads of trading firms). The organizing principle for the community will vary, but the members of the community generally share similar security, privacy, performance and compliance requirements. It is designed to serve a specific community of users who collaborate, share resources, and often have common security and compliance requirements.
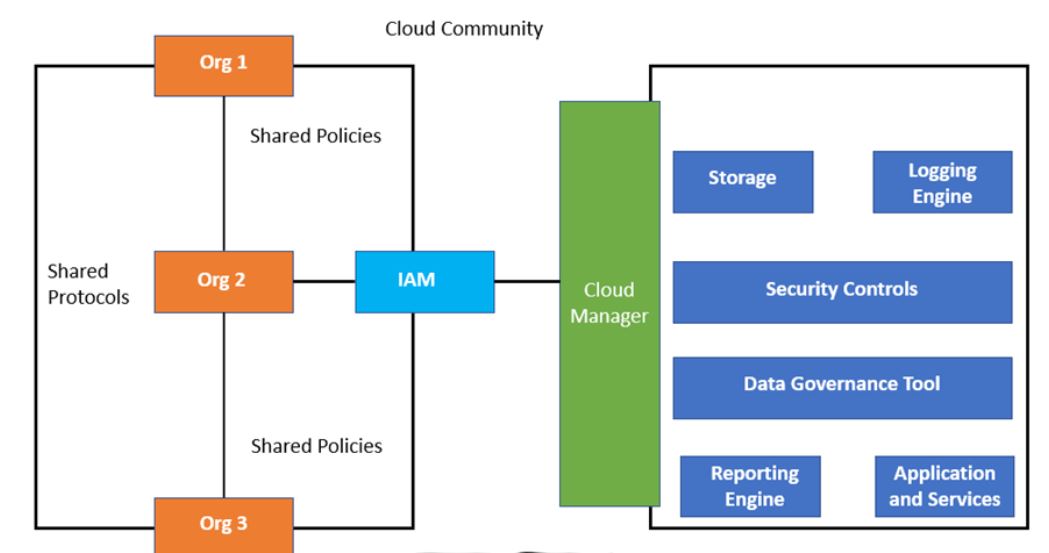
Members of the community cloud are essentially organizations with similar business needs. These business requirements are derived from the industry regulations along with the need for shared data and services.
Here are all the entities of community cloud architecture.
In the above image, they are represented as “Org 1”, “Org2”, and “Org 3,” respectively. Such organizations generally have shared policies and protocols. IAM is an abbreviation for identity and access management that provides authorization and access to the specific cloud that meets the shared protocols and policies adopted by different organizations. Cloud manager is an entity that becomes an interface for different organizations to manage their shared resources and protocols. Storage requirements is Different clouds may offer separate storage in accordance with the requirements of different organizations. They are documented under the service level agreements of the community cloud.
Advantages of Community Clouds
- Cost Sharing - Community cloud members can benefit from cost-sharing, which can lead to reduced infrastructure and operational costs. Since multiple organizations share the expenses, each member can access advanced cloud services at a fraction of the cost of building and maintaining a private cloud.
- Customization - Community clouds allow for a higher degree of customization compared to public clouds. Members can tailor the cloud environment to meet their specific needs, including security, compliance, and performance requirements.
- Security and Compliance - Community clouds are often designed with robust security features and controls to meet the specific compliance requirements of the community members. This makes them well-suited for industries with strict regulatory mandates, such as healthcare or finance.
- Collaboration - Members of a community cloud often have shared goals and interests, making collaboration and data sharing more seamless and efficient. This can lead to increased productivity and innovation within the community.
- Managed Services - Community clouds are typically managed by third-party providers, relieving community members from the burden of infrastructure management, maintenance, and upgrades. This allows organizations to focus on their core competencies.
- Data Isolation - Community clouds provide a higher level of data isolation and privacy compared to public clouds. Data from one organization is logically separated from others, enhancing data security and confidentiality.
- Scalability - Community clouds can be designed to scale as the community grows. New organizations or users can join the community, and the cloud infrastructure can expand to accommodate increased demand.
Disadvantages of Community Clouds
- Limited Audience - Community clouds are not suitable for all organizations since they are tailored to specific communities with shared interests. Organizations outside the defined community may not be able to access or benefit from the cloud resources.
- Complex Governance - Managing the governance and decision-making processes within a community cloud can be challenging. It requires coordination and agreement among community members on various aspects, such as resource allocation, security policies, and service levels.
- Dependency on Service Provider - Community cloud members rely on a third-party service provider to maintain and operate the infrastructure. This dependency can lead to issues if the provider experiences service disruptions, security breaches, or other operational problems.
- Potential for Resource Contention - Since multiple organizations share the same infrastructure, there is a risk of resource contention during peak usage periods. This can affect the performance of cloud services and applications.
- Data Residency Concerns - Depending on the location of the community cloud's data centers, data residency and sovereignty issues may arise, especially if data must comply with specific regional or national regulations.
- Cost Sharing Challenges - While cost-sharing is an advantage, it can also be a disadvantage if there is a lack of fairness or transparency in how costs are allocated among community members. Disputes over cost sharing can strain relationships within the community.
5. Multi Cloud
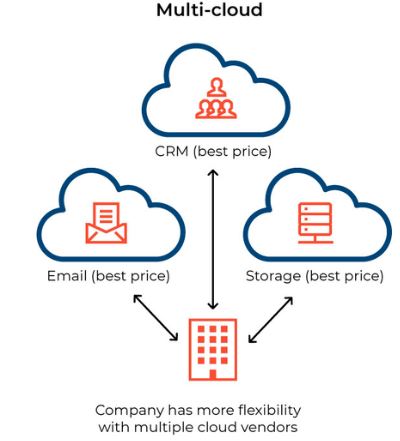
Multicloud computing, as this word suggests, is the use of multiple public cloud services from different vendors within one architecture at the same time. Multi-cloud is a cloud computing strategy that involves using multiple cloud service providers to meet an organization's computing and storage needs. Instead of relying on a single cloud provider, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform (GCP), organizations adopt a multi-cloud approach to leverage the strengths and capabilities of multiple cloud providers.
A common example would be the use of public cloud services such as Google Drive and Dropbox to store and transfer documents.
Advantages of Multi Cloud
- Vendor Independence - By using multiple cloud providers, organizations can avoid vendor lock-in and maintain negotiating power when dealing with providers.
- Redundancy and Resilience - Multi-cloud setups enhance redundancy and resilience. If one provider experiences an outage, workloads can be shifted to another provider to maintain service availability.
- Cost Optimization - Organizations can choose the most cost-effective cloud services for specific use cases, potentially reducing overall cloud spending.
- Geographical Diversity - Multi-cloud allows organizations to store data in specific geographic regions or data centers to meet regulatory and data sovereignty requirements.
- Improved Performance - By deploying resources closer to end-users or specific geographic regions, organizations can potentially improve application performance and reduce latency.
- Best-of-Breed Services - Organizations can select the best cloud services from different providers for their unique needs, taking advantage of each provider's strengths.
- Risk Mitigation - Distributing workloads across multiple cloud providers can help mitigate risks associated with service outages, security vulnerabilities, or changes in a single provider's offerings.
- Hybrid Cloud Integration - Multi-cloud can seamlessly integrate with on-premises data centers and hybrid cloud deployments, providing a unified approach to managing both cloud and on-premises resources.
Disadvantages of Multi Cloud
- Complexity - Managing multiple cloud providers can be complex, requiring expertise in each platform, which can lead to increased operational complexity and potential skill gaps.
- Cost Management - While multi-cloud can optimize costs, it can also introduce challenges in tracking and managing spending across different providers.
- Data and Application Portability - Ensuring that data and applications can move seamlessly between different clouds can be challenging and may require additional development efforts.
- Security and Compliance - Managing security and compliance across multiple cloud environments can be more complex, as each provider may have its own set of security tools and compliance standards.
- Interoperability - Integrating services and data between different cloud providers may require custom development and may not always be straightforward.
- Vendor-Specific Tools - Organizations may become reliant on vendor-specific tools and APIs, making it harder to switch providers in the future.
- Resource Fragmentation - Without careful management, resources can become fragmented across multiple providers, making it difficult to track and optimize resource utilization.
- Vendor Relationships - Managing relationships with multiple cloud providers can be time-consuming and require dedicated vendor management.
Next
