C# - Operators
An operator performs some operation on single or multiple operands (data value) and produces a result. Operators are symbols or keywords that instruct the C# engine to take certain actions. The addition (+) sign, for example, instructs the C# engine to add two variables or values, whereas the equal-to (=), greater-than (>), or less-than (<) symbols instruct the compiler to compare two variables or values, and so on.
Let us take a simple expression 3 + 5 is equal to 8. Here, 3 and 5 are called operands and "+" is called the operator.
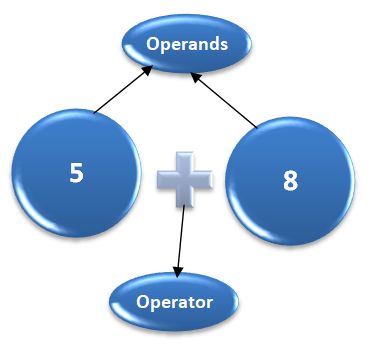
C# contains both unary (single operand) and binary operators (two operands).
Unary operator - Operand operator or Operator operand
Example
a++ or ++a
Binary operator -Operand operator operand
Example
a * b
The following operators are available in C#.
- Arithmetic Operators
- Assignment Operators
- Comparison (Relational) Operators
- Bitwise Operators
- Logical Operators
1. Arithmetic Operators in C#
Arithmetic Operators are used to perform arithmetic on numbers or operands.
The following table show the list of arithmatic operators in C#.
| SNo. | Operator | Type | Description with Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Addition (+) | Binary | It is used to return the value after addition. ex- (20 + 30) |
| 2 | Subtraction (-) | Binary | It is used to return the value after subtraction. ex- (30 - 20) |
| 3 | Multiplication (*) | Binary | It is used to return the value after multiplying the operands. ex- (30 * 20) |
| 4 | Division (/) | Binary | It is used to return the value after dividing 2 operands. ex- (30 / 3) |
| 5 | Remainder (%) | Binary | It is used to return the integer remainder after dividing 2 operands. ex- (30 % 4) |
| 6 | Increment (++) | Unary | It adds 1 to the operand. For the prefix operator (++var2), it returns the value after adding 1. For the postfix operator (var2++), it adds 1 to the value then returns it. ex- 7++ |
| 7 | Decrement (--) | Unary | It subtracts 1 from the operand. For the prefix operator (–var2), it returns the value after subtracting 1. For the postfix operator (var2–), it subtracts 1 from the value then returns it. ex- 7-- |
You can paste the below code in VisualStudio editor and run the program.
using System;
namespace FirstProgram
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
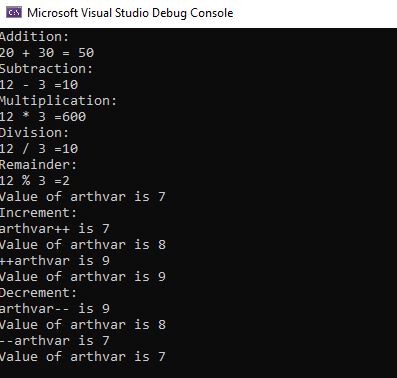
Console.WriteLine("Addition:");
Console.WriteLine("20 + 30 = " + (20 + 30) );
Console.WriteLine("Subtraction:");
Console.WriteLine("12 - 3 =" + (30 - 20) );
Console.WriteLine("Multiplication:");
Console.WriteLine("12 * 3 =" + (30 * 20) );
Console.WriteLine("Division:");
Console.WriteLine("12 / 3 =" + (30 / 3) );
Console.WriteLine("Remainder:");
Console.WriteLine("12 % 3 =" + (30 % 4) );
var arthvar = 7;
Console.WriteLine("Value of arthvar is " +arthvar);
Console.WriteLine("Increment:");
Console.WriteLine("arthvar++ is " + (arthvar++) );
Console.WriteLine("Value of arthvar is " + arthvar );
Console.WriteLine("++arthvar is " + (++arthvar) );
Console.WriteLine("Value of arthvar is " + arthvar );
Console.WriteLine("Decrement:");
Console.WriteLine("arthvar-- is " + (arthvar--));
Console.WriteLine("Value of arthvar is " + arthvar );
Console.WriteLine("--arthvar is " + (--arthvar));
Console.WriteLine("Value of arthvar is " + arthvar );
}
}
}Output
2. Assignment Operators in C#
An assignment operator is used to assigns a value to the left operand based on the value of its right operand with the help of equals = sign.
The following table show the list of Assignment operators in C#.
| SNo. | Operator | Description | Shorthand | Meaning | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | = | Assignment | x = y | x = y | |
| 2 | += | Add and Assignment | x += y | x = x + y | |
| 3 | -= | Subtract and Assignment | x -= y | x = x - y | |
| 4 | *= | Multiply and Assignment | x *= y | x = x * y | |
| 5 | /= | Division Assignment | x /= y | x = x / y | |
| 6 | %= | Remainder Assignment | x %= y | x = x % y |
You can paste the below code in VisualStudio editor and run the program.
using System;
namespace FirstProgram
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
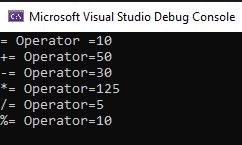
var a=0;
a = 10;
Console.WriteLine("= Operator =" + a );
a = 20;
a += 30;
Console.WriteLine("+= Operator=" + a );
a = 50;
a -= 20;
Console.WriteLine("-= Operator=" + a );
a = 5;
a *= 25;
Console.WriteLine("*= Operator=" + a );
a = 50;
a /= 10;
Console.WriteLine("/= Operator=" + a );
a = 100;
a %= 15;
Console.WriteLine("%= Operator=" + a);
}
}
}Output
3. Comparison Operators
A comparison operator compares its operands and returns a boolean value (true or false) based on whether the comparison is true.
The following table show the list of Comparison operators in C#.
| SNo. | Operator | Name | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | == | Equal | x == y | True if x is equal to y |
| 2 | != | Not equal | x != y | True if x is not equal to y |
| 3 | < | Less than | x < y | True if x is less than y |
| 4 | > | Greater than | x > y | True if x is greater than y |
| 5 | >= | Greater than or equal to | x >= y | True if x is greater than or equal to y |
| 6 | <= | Less than or equal to | x <= y | True if x is less than or equal to y |
You can paste the below code in VisualStudio editor and run the program.
using System;
namespace FirstProgram
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
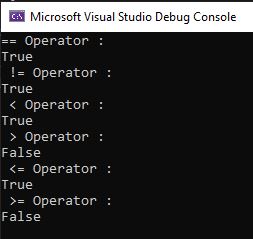
int x = 35;
int y = 45;
int z = 35;
Console.WriteLine("== Operator : ");
Console.WriteLine(x == z);
Console.WriteLine(" != Operator : ");
Console.WriteLine(x != y);
Console.WriteLine(" < Operator : ");
Console.WriteLine(x < y);
Console.WriteLine(" > Operator : ");
Console.WriteLine(x > y);
Console.WriteLine(" <= Operator : ");
Console.WriteLine(x <= y);
Console.WriteLine(" >= Operator : ");
Console.WriteLine(x >= y);
}
}
}
Output
4. Bitwise Operators
The bitwise operators perform bitwise operations on operands. The bitwise operators are as follows:
| SNo. | Operator | Name | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | & | Bitwise AND | (10==20 & 20==33) = 0 | It returns 1 if both operands are ones |
| 2 | | | Bitwise OR | (10==20 | 20==33) = 0 | It returns 0 if both operands are zero |
| 3 | ^ | Bitwise XOR | (10==20 ^ 20==33) = 0 | It returns 0 in each bit position for which the corresponding bits are the same and 1 in each bit position for which the corresponding bits are different. |
| 4 | ~ | Bitwise NOT | (~10) = -11 | The operand's bits are inverted by it. |
| 5 | << | Bitwise Left Shift | (10<<2) = 40 | It shifts x in binary representation y bits to the left, shifting in zeros from the right. |
| 6 | >> | Bitwise Right Shift | (10>>2) = 2 | It shifts x in binary representation y bits to the right, discarding bits shifted off. |
You can paste the below code in VisualStudio editor and run the program.
using System;
namespace FirstProgram
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
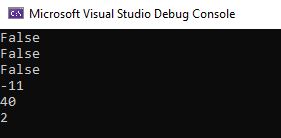
Console.WriteLine(10 == 20 & 20 == 33);
Console.WriteLine(10 == 20 | 20 == 33);
Console.WriteLine(10 == 20 ^ 20 == 33);
Console.WriteLine(~10);
Console.WriteLine(10 << 2);
Console.WriteLine(10 >> 2);
}
}
}
Output
5. Logical Operators
These operators are (typically) used with Boolean/ logical values and return a Boolean value. However, if the && and || operators are used with non-Boolean values, they may return a non-Boolean value.
The following table show the list of Logical operators in C#.
| SNo. | Operator | Name | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | && |
And | x && y |
True if both x and y are true |
| 2 | || |
Or | x || y |
True if either x or y is true |
| 3 | ! |
Not | !x |
True if x is not true |
You can paste the below code in VisualStudio editor and run the program.
using System;
namespace FirstProgram
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var x = 8;
var y = 3;
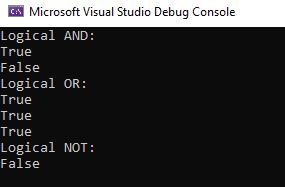
Console.WriteLine("Logical AND:");
Console.WriteLine(x < 10 && y > 1);
Console.WriteLine(x < 10 && y < 1);
Console.WriteLine("Logical OR:");
Console.WriteLine(x < 10 || y > 1);
Console.WriteLine(x < 10 || y > 1);
Console.WriteLine(x < 10 || y < 1);
Console.WriteLine("Logical NOT:");
Console.WriteLine(!(x > y));
}
}
}Output
Prev Next
