C# - DataTypes
C# is a strongly-typed language. It means we must declare the type of a variable. C# has several built-in data types that can be used to store different types of values. These data types can be broadly classified into the following categories. They are Value Types , Reference Types and Pointer Types . The Value Types store the data while the Reference Types store references to the actual data. Pointer Types variable use only in unsafe mode. The Value Types derived from System.ValueType and the Reference Types derived from System.Object .
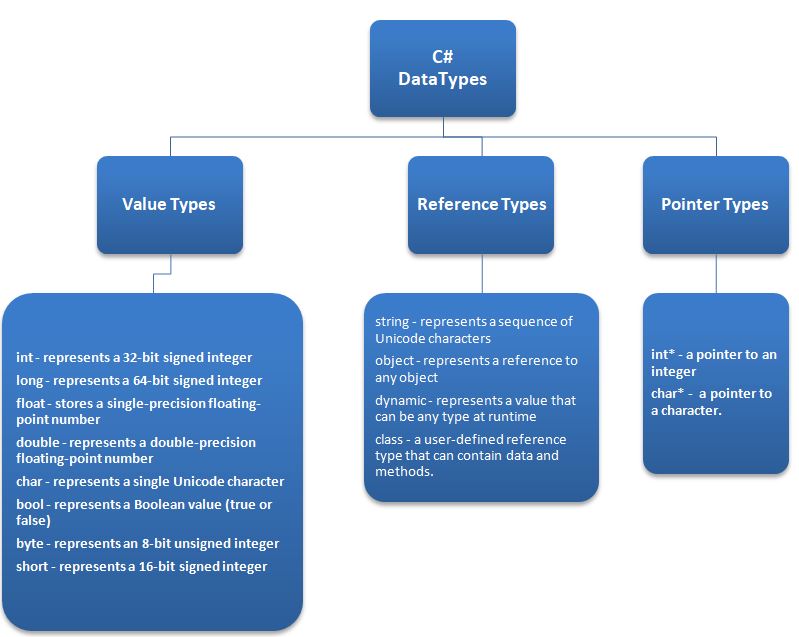
Types of C# DataTypes
- Value types
- Reference types
- Pointer types
1. Value types
These are data types that store their value directly in memory. They are typically used for simple types of data like numbers, bool and characters.
| Data Type | Description |
|---|---|
| int | It represents a 32-bit signed integer |
| long | It represents a 64-bit signed integer |
| float | It stores a single-precision floating-point number. |
| double | It represents a double-precision floating-point number |
| char | It represents a single Unicode character |
| bool | It represents a Boolean value (true or false) |
| byte | It represents an 8-bit unsigned integer |
| short | It represents a 16-bit signed integer |
2. Reference types
These are data types that store a reference to an object in memory. They are typically used for more complex types of data like strings and arrays.
Examples
| Data Type | Description |
|---|---|
| string | It represents a sequence of Unicode characters |
| object | It represents a reference to any object |
| dynamic | It represents a value that can be any type at runtime |
| class | It a user-defined reference type that can contain data and methods. |
3. Pointer types
These are data types that store a memory address. They are used in low-level programming and are not commonly used in C#.
Following is the syntax of declaring the pointer type in the c# programming language.
- int*: a pointer to an integer
- char*: a pointer to a character.
Prev Next
